Tracking ShadowPad Infrastructure Via Non-Standard Certificates
Tracking ShadowPad Infrastructure Via Non-Standard Certificates
Published on
Feb 9, 2024

This post will examine ShadowPad infrastructure linked to a yet-to-be-identified threat actor. What makes this activity different is a slight change in the HTTP response headers and the use of a certificate attempting to spoof American technology company, Dell. Within this group of IPs, there are additional subsets of activity utilizing different port configurations and some interesting domains, discussed later in this article.
Thanks to Greg & Cal for answering my questions regarding this infrastructure.
Out With The Old?
Stay with me if you're already familiar with detecting ShadowPad using the standard HTTP headers with Nginx servers and TLS certificates using my* fields.
ShadowPad is a modular trojan shared privately by several suspected state-linked Chinese threats since 2019. It has been used in network intrusions focused on espionage, information theft, and even financial gain.
See Figures 1 & 2 below for examples of recently identified ShadowPad infrastructure.
*These servers and many more are tagged and available to Hunt users. Apply for an account today, and let us know what you think.
One could quickly start tracking servers with the above information (in addition to other factors such as provider, location, domains, etc. ) and add them to network blocklists. The only problem with this approach is that focusing on an oft-seen certificate will prevent defenders from missing minor changes to similar infrastructure.
Let's look at what made this set of IP addresses stand out from the others.
What's The Difference?
We've identified over 30 servers using the spoofed Dell certificate from across the internet. Note: The ports listed utilize the cert and do not indicate overall ports found on each IP address.
There are two ways to dig into this infrastructure: via the Advanced Search feature (below) or as part of the more extensive set of ShadowPad servers Hunt tracks, pictured in Figure 4.
All fields of the certificate are listed below:
C=US, ST=Texas, L=Round Rock, O=Dell Technologies Inc., OU=Dell Data Vault, CN=Dell Technologies Inc.
The HTTP headers in Figure 6 should look familiar. When combined with the previously described additional factors and third-party intelligence (Recorded Future & VirusTotal), we have confirmation that we are on the trail of an actor(s) using ShadowPad.
Cracking The Dell Data Vault
None of the IP addresses identified as linked to the malware are consecutively assigned, which could indicate a threat actor purchasing the servers from a reseller. However, many are closely related, which shows a strong preference for one provider over others.
Figures 7 and 8 below show the providers making up the infrastructure, as well as the geolocations of the servers.
Suspected Cluster #1
Ports utilized for likely C2 communication consist of common ports: 53, 80, 443, 8080, 8443, 44444. While port 53 is nothing new when discussing malware communicating with a controller, just 12 IPs out of the 30+ identified have the port exposed as an HTTP server with an Nginx header (Figure 9).
Without malware samples and additional information to analyze, this anomaly has three possible motives:
1 Targeted Deployment: Standard C2 ports are used for most servers. However, this subset could represent a high-value target, where leveraging port 53 is believed to bypass detection.
2 Possible Misconfiguration: This could be an unintentional mistake made during server setup.
3 Second or Third Actor: The servers using port 53 may belong to a separate actor. While the 31 IPs identified share similarities, this subset might be part of a separate operation utilizing specific tactics and tools.
Of course, all three of the above could be wrong. There may be a part 2 to this post.
IP addresses and domains of this suspected cluster are below.
| IP Address | Domain | ASN | Cert Last Seen |
|---|---|---|---|
| 45.76.146.215 | app2[.]toggle2[.]com | The Constant Company | 2024-02-06 |
| 81.68.102.11 | N/A | Tencent | 2024-02-06 |
| 47.254.251.168 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-01-30 |
| 139.180.188.54 | update[.]performed12.com www[.]fadfar[.]com kzb[.]performed12[.]com time[.]afsder[.]com updata[.]dsqueryonline[.]com microsoft[.]performed12[.]com updata[.]installation77[.]com az[.]performed12[.]com time[.]kkdiscover[.]com update[.]kkdiscover[.]com power[.]installation77[.]com | The Constant Company | 2024-02-06 |
| 8.217.107.25 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-05 |
| 38.60.193.62 | N/A | Kaopou Cloud HK | 2024-02-05 |
| 38.54.105.226 | microsoft[.]kiwi[.]nz www[.]kazakhtelecom[.]zzux[.]com kazakhtelecom[.]zzux[.]com google[.]org[.]im www[.]google[.]org[.]im turkeylahainasunset[.]com www[.]microsoft[.]kiwi[.]nz | Kaopou Cloud HK | 2024-02-04 |
| 108.61.163.91 | czs[.]superdasqe[.]me | The Constant Company | 2024-02-06 |
| 47.243.60.4 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-02 |
| 8.218.214.23 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-02 |
| 8.218.248.158 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-01-26 |
| 8.218.163.77 | mirco[.]supermirco[.]us mircoo[.]supermirco[.]us | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-04 |
| 47.242.52.22 | update[.]micro[.]gay ns[.]supermirco[.]us shaduruanjian8[.]com img[.]shaduruanjian8[.]com www[.]shaduranjian8[.]com m[.]shadurauanjian8[.]com update[.]imiul[.]com | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-06 |
Table 1: Port 53 cluster IPs, domains, ASN, and certificate last seen dates
Theory #1 could be a possibility when looking at the domains in Table 1 compared to the rest. The following entities are being spoofed:
Microsoft
KazakhTelecom -- and Kazakhstan's largest telecom company.
Google
SuperMicro -- A US IT company with offices in The Netherlands & Taiwan.
Shaduruanjian -- Translates to "antivirus software" from Chinese.
Suspected Cluster #2:
I don't feel as strongly about this suspected cluster as the first, but it's interesting enough from the rest of the IPs that it's still worth putting out there for other researchers to dig into. All servers identified in Hunt share similar ports, 53, 80, etc., except for five, which only use port 443 for ShadowPad. The IPs in question are listed below.
| IP Address | Domain | ASN | Cert Last Seen |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8.217.96.167 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-01-28 |
| 149.28.135.145 | N/A | The Constant Company | 2024-01-24 |
| 45.76.84.222 | N/A | The Constant Company | 2024-01-31 |
| 45.32.127.56 | www[.]bernaspos[.]com bernaspos[.]com | The Constant Company | 2024-01-31 |
| 185.81.114.45 | pitikytech[.]me mail[.]pitikytech[.]me | HZ Hosting Ltd | 2024-01-18 |
Table 2: Smaller possible cluster using only port 443
Bonus
The spoofed Dell certificates weren't the only interesting information found when looking at this infrastructure. Many servers utilized a pattern of common names for RDP. For example, "iZ5qjajwc0tiohZ" was seen amongst 11 IPs and not associated with the port 53 cluster.
Additional RDP CNs are listed below.
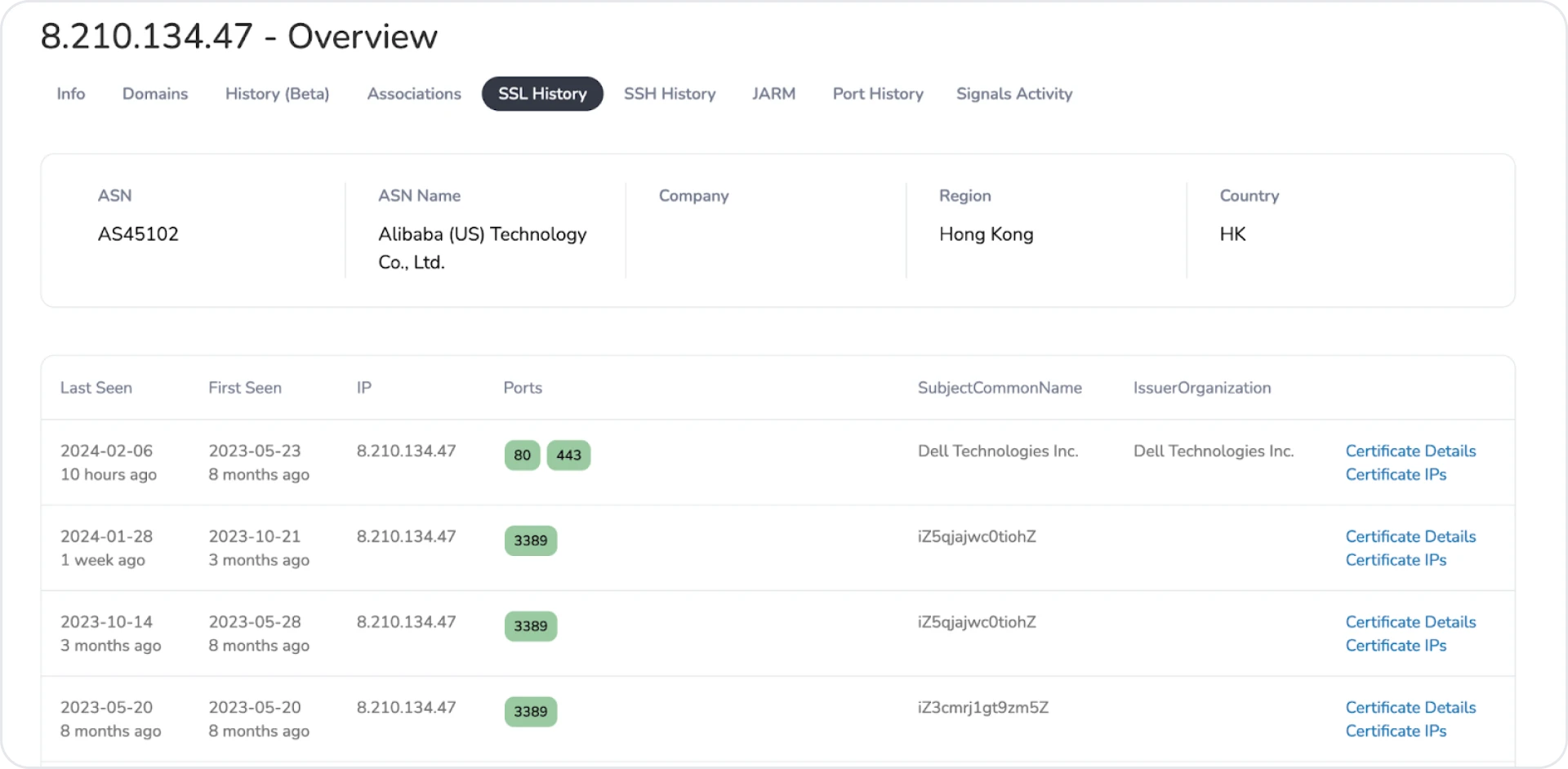 Figure 11: First example of interesting RDP cert common name
Figure 11: First example of interesting RDP cert common name 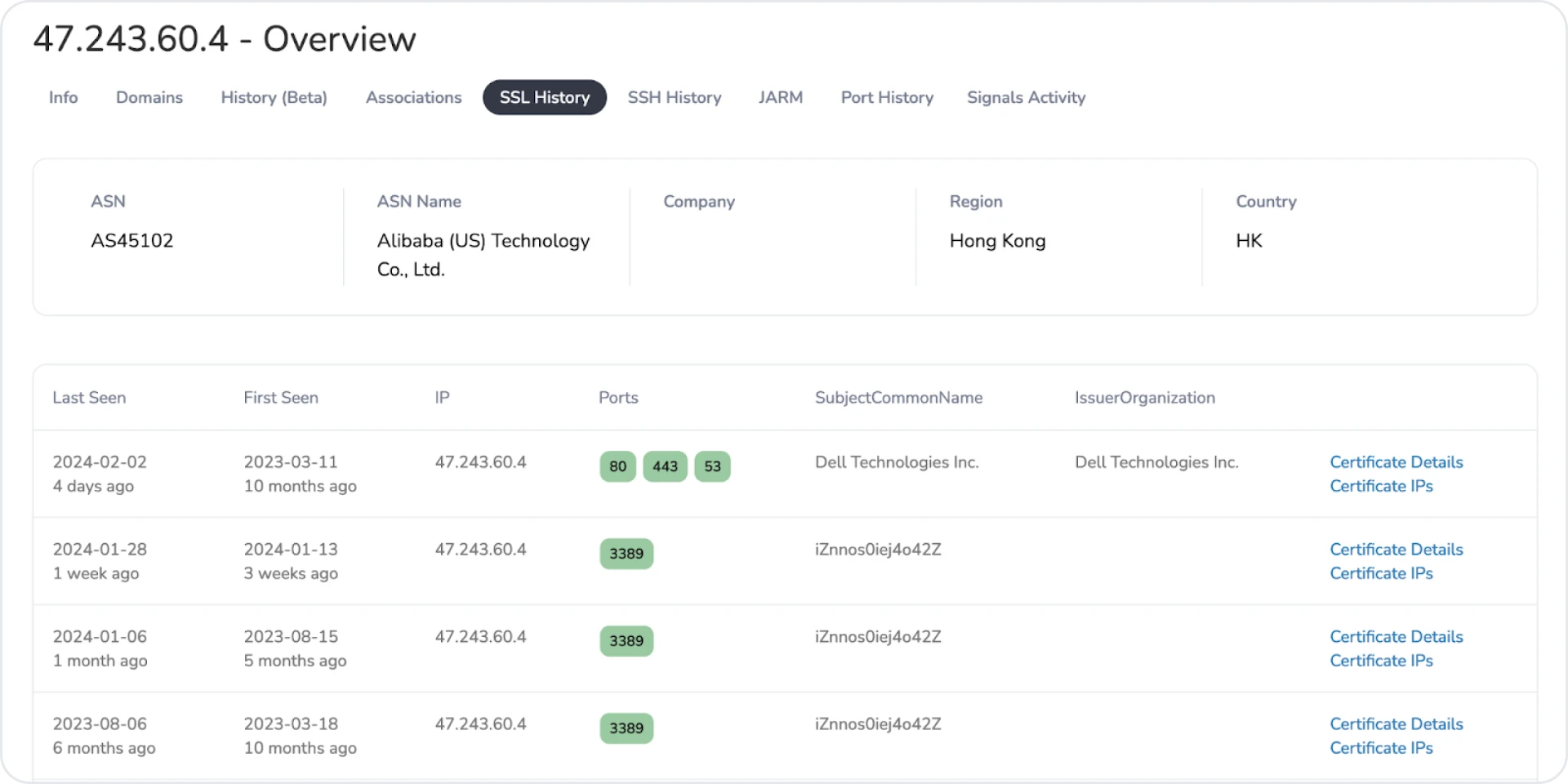 Figure 12: Another example of RDP cert
Figure 12: Another example of RDP cert 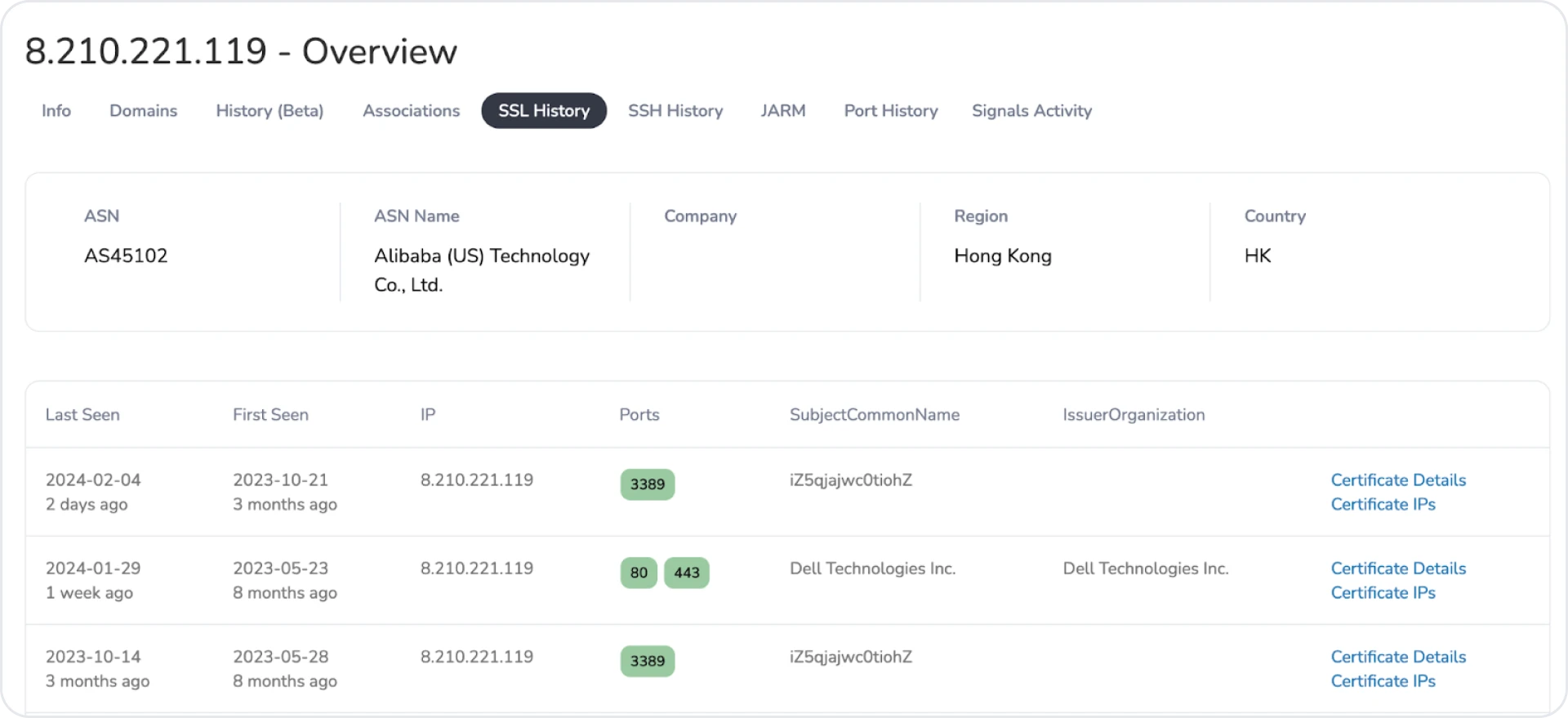 Figure 13: Final example of similar RDP certificates
Figure 13: Final example of similar RDP certificates Conclusion
Hopefully, you enjoyed this post highlighting how looking outside default detection signatures can unveil malicious infrastructure. While most servers relied on standard communication ports, an interesting subset of 12 IPs utilized an HTTP server on port 53, raising questions about targeted deployment or misconfigurations.
If you haven't already, apply for an account and join me in researching additional ShadowPad servers.
Remaining IPs/Domains
| IP Address | Domain | ASN | Cert Last Seen |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8.210.74.92 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-01-31 |
| 8.218.17.11 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-06 |
| 43.153.92.190 | N/A | Tencent | 2024-02-06 |
| 8.218.56.204 | api[.]sourcedata[.]kuwannba[.]com | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-06 |
| 8.217.0.193 | update[.]imjzo[.]com | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-06 |
| 8.218.244.117 | ayana[.]imiul[.]com icw[.]imiul[.]com | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-01 |
| 139.84.168.128 | update[.]alpha-els[.]com | The Constant Company | 2024-01-31 |
| 146.70.92.137 | N/A | M247 Europe | 2024-01-28 |
| 8.217.84.192 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-01 |
| 8.210.174.168 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-04 |
| 8.210.168.192 | wagodo[.]imiul[.]com | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-01 |
| 8.210.134.47 | www[.]stdhgd[.]com wait[.]imiul[.]com | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-06 |
| 8.210.221.119 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-01-29 |
| 8.218.128.35 | wapaku[.]imiul[.]com | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-02 |
| 8.218.213.245 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-06 |
| 5.34.176.152 | foligni[.]it mails[.]foligni[.]it | Green Floid LLC | 2024-01-18 |
This post will examine ShadowPad infrastructure linked to a yet-to-be-identified threat actor. What makes this activity different is a slight change in the HTTP response headers and the use of a certificate attempting to spoof American technology company, Dell. Within this group of IPs, there are additional subsets of activity utilizing different port configurations and some interesting domains, discussed later in this article.
Thanks to Greg & Cal for answering my questions regarding this infrastructure.
Out With The Old?
Stay with me if you're already familiar with detecting ShadowPad using the standard HTTP headers with Nginx servers and TLS certificates using my* fields.
ShadowPad is a modular trojan shared privately by several suspected state-linked Chinese threats since 2019. It has been used in network intrusions focused on espionage, information theft, and even financial gain.
See Figures 1 & 2 below for examples of recently identified ShadowPad infrastructure.
*These servers and many more are tagged and available to Hunt users. Apply for an account today, and let us know what you think.
One could quickly start tracking servers with the above information (in addition to other factors such as provider, location, domains, etc. ) and add them to network blocklists. The only problem with this approach is that focusing on an oft-seen certificate will prevent defenders from missing minor changes to similar infrastructure.
Let's look at what made this set of IP addresses stand out from the others.
What's The Difference?
We've identified over 30 servers using the spoofed Dell certificate from across the internet. Note: The ports listed utilize the cert and do not indicate overall ports found on each IP address.
There are two ways to dig into this infrastructure: via the Advanced Search feature (below) or as part of the more extensive set of ShadowPad servers Hunt tracks, pictured in Figure 4.
All fields of the certificate are listed below:
C=US, ST=Texas, L=Round Rock, O=Dell Technologies Inc., OU=Dell Data Vault, CN=Dell Technologies Inc.
The HTTP headers in Figure 6 should look familiar. When combined with the previously described additional factors and third-party intelligence (Recorded Future & VirusTotal), we have confirmation that we are on the trail of an actor(s) using ShadowPad.
Cracking The Dell Data Vault
None of the IP addresses identified as linked to the malware are consecutively assigned, which could indicate a threat actor purchasing the servers from a reseller. However, many are closely related, which shows a strong preference for one provider over others.
Figures 7 and 8 below show the providers making up the infrastructure, as well as the geolocations of the servers.
Suspected Cluster #1
Ports utilized for likely C2 communication consist of common ports: 53, 80, 443, 8080, 8443, 44444. While port 53 is nothing new when discussing malware communicating with a controller, just 12 IPs out of the 30+ identified have the port exposed as an HTTP server with an Nginx header (Figure 9).
Without malware samples and additional information to analyze, this anomaly has three possible motives:
1 Targeted Deployment: Standard C2 ports are used for most servers. However, this subset could represent a high-value target, where leveraging port 53 is believed to bypass detection.
2 Possible Misconfiguration: This could be an unintentional mistake made during server setup.
3 Second or Third Actor: The servers using port 53 may belong to a separate actor. While the 31 IPs identified share similarities, this subset might be part of a separate operation utilizing specific tactics and tools.
Of course, all three of the above could be wrong. There may be a part 2 to this post.
IP addresses and domains of this suspected cluster are below.
| IP Address | Domain | ASN | Cert Last Seen |
|---|---|---|---|
| 45.76.146.215 | app2[.]toggle2[.]com | The Constant Company | 2024-02-06 |
| 81.68.102.11 | N/A | Tencent | 2024-02-06 |
| 47.254.251.168 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-01-30 |
| 139.180.188.54 | update[.]performed12.com www[.]fadfar[.]com kzb[.]performed12[.]com time[.]afsder[.]com updata[.]dsqueryonline[.]com microsoft[.]performed12[.]com updata[.]installation77[.]com az[.]performed12[.]com time[.]kkdiscover[.]com update[.]kkdiscover[.]com power[.]installation77[.]com | The Constant Company | 2024-02-06 |
| 8.217.107.25 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-05 |
| 38.60.193.62 | N/A | Kaopou Cloud HK | 2024-02-05 |
| 38.54.105.226 | microsoft[.]kiwi[.]nz www[.]kazakhtelecom[.]zzux[.]com kazakhtelecom[.]zzux[.]com google[.]org[.]im www[.]google[.]org[.]im turkeylahainasunset[.]com www[.]microsoft[.]kiwi[.]nz | Kaopou Cloud HK | 2024-02-04 |
| 108.61.163.91 | czs[.]superdasqe[.]me | The Constant Company | 2024-02-06 |
| 47.243.60.4 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-02 |
| 8.218.214.23 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-02 |
| 8.218.248.158 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-01-26 |
| 8.218.163.77 | mirco[.]supermirco[.]us mircoo[.]supermirco[.]us | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-04 |
| 47.242.52.22 | update[.]micro[.]gay ns[.]supermirco[.]us shaduruanjian8[.]com img[.]shaduruanjian8[.]com www[.]shaduranjian8[.]com m[.]shadurauanjian8[.]com update[.]imiul[.]com | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-06 |
Table 1: Port 53 cluster IPs, domains, ASN, and certificate last seen dates
Theory #1 could be a possibility when looking at the domains in Table 1 compared to the rest. The following entities are being spoofed:
Microsoft
KazakhTelecom -- and Kazakhstan's largest telecom company.
Google
SuperMicro -- A US IT company with offices in The Netherlands & Taiwan.
Shaduruanjian -- Translates to "antivirus software" from Chinese.
Suspected Cluster #2:
I don't feel as strongly about this suspected cluster as the first, but it's interesting enough from the rest of the IPs that it's still worth putting out there for other researchers to dig into. All servers identified in Hunt share similar ports, 53, 80, etc., except for five, which only use port 443 for ShadowPad. The IPs in question are listed below.
| IP Address | Domain | ASN | Cert Last Seen |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8.217.96.167 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-01-28 |
| 149.28.135.145 | N/A | The Constant Company | 2024-01-24 |
| 45.76.84.222 | N/A | The Constant Company | 2024-01-31 |
| 45.32.127.56 | www[.]bernaspos[.]com bernaspos[.]com | The Constant Company | 2024-01-31 |
| 185.81.114.45 | pitikytech[.]me mail[.]pitikytech[.]me | HZ Hosting Ltd | 2024-01-18 |
Table 2: Smaller possible cluster using only port 443
Bonus
The spoofed Dell certificates weren't the only interesting information found when looking at this infrastructure. Many servers utilized a pattern of common names for RDP. For example, "iZ5qjajwc0tiohZ" was seen amongst 11 IPs and not associated with the port 53 cluster.
Additional RDP CNs are listed below.
 Figure 11: First example of interesting RDP cert common name
Figure 11: First example of interesting RDP cert common name  Figure 12: Another example of RDP cert
Figure 12: Another example of RDP cert  Figure 13: Final example of similar RDP certificates
Figure 13: Final example of similar RDP certificates Conclusion
Hopefully, you enjoyed this post highlighting how looking outside default detection signatures can unveil malicious infrastructure. While most servers relied on standard communication ports, an interesting subset of 12 IPs utilized an HTTP server on port 53, raising questions about targeted deployment or misconfigurations.
If you haven't already, apply for an account and join me in researching additional ShadowPad servers.
Remaining IPs/Domains
| IP Address | Domain | ASN | Cert Last Seen |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8.210.74.92 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-01-31 |
| 8.218.17.11 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-06 |
| 43.153.92.190 | N/A | Tencent | 2024-02-06 |
| 8.218.56.204 | api[.]sourcedata[.]kuwannba[.]com | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-06 |
| 8.217.0.193 | update[.]imjzo[.]com | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-06 |
| 8.218.244.117 | ayana[.]imiul[.]com icw[.]imiul[.]com | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-01 |
| 139.84.168.128 | update[.]alpha-els[.]com | The Constant Company | 2024-01-31 |
| 146.70.92.137 | N/A | M247 Europe | 2024-01-28 |
| 8.217.84.192 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-01 |
| 8.210.174.168 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-04 |
| 8.210.168.192 | wagodo[.]imiul[.]com | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-01 |
| 8.210.134.47 | www[.]stdhgd[.]com wait[.]imiul[.]com | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-06 |
| 8.210.221.119 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-01-29 |
| 8.218.128.35 | wapaku[.]imiul[.]com | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-02 |
| 8.218.213.245 | N/A | Alibaba (US) | 2024-02-06 |
| 5.34.176.152 | foligni[.]it mails[.]foligni[.]it | Green Floid LLC | 2024-01-18 |
Related Posts
Related Posts
Related Posts


