IOC feeds provide real-time data to spot and counter cyber threats. But keeping up with this flood of information is no small task; in fact, the average security analyst spends 2-4 hours every day sifting through threat intelligence, according to market.us.
And the pressure is only growing: the Identity Theft Resource Center (ITRC) reported 1,732 data compromises in just the first half of 2026, impacting nearly 166 million people.
With the right IOC feeds, however, you can cut through the noise, act faster, and strengthen your defenses.
That's why in this article, we'll walk through the top 10 IOC feeds for 2026, explain their role in threat detection, and help you choose the ones that deliver the most impact for your cybersecurity strategy.
The Basics: What are IOC Feeds?
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) are forensic artifacts that signal potential network breaches or intrusions. Microsoft defines them as "evidence that someone may have breached an organization's network or endpoint."

These artifacts are warning signs, alerting security teams regarding malicious activity that could compromise system integrity. Using them effectively is key to proactive defense and rapid incident response, so you can detect breaches in days, not weeks.
IOC feeds are streams of data that provide real-time information about potential threats. This continuous flow of threat-related data helps you tackle cybercriminals by identifying and mitigating threats at different stages of the attack lifecycle, from reconnaissance to exploitation. Monitoring these feeds helps with proactive threat hunting, so security teams can find advanced threats before they cause damage.
Analyzing IOCs regularly helps you find security gaps and refine your defenses. This not only improves your overall security but also helps with compliance. Tangible evidence provided by IOCs like malicious IP addresses or unusual login attempts is gold in incident detection and response.
Now that we've covered what IOC feeds are and why they matter, let's look at why relying on just one feed isn't enough.
Why You Need More Than One IOC Feed
Using multiple IOC feeds is essential to get a full picture of the threat landscape. Different feeds have different data collection methods, so they provide different insights that enhance overall threat detection. This diversity helps prevent data gaps, so you're not relying on a single source for threat intelligence.
Including multiple feeds allows for cross-referencing of information, which validates indicators and makes the data more relevant. This helps security teams prioritize threats so they can respond faster and more effectively to potential threats. Customizing IOC feed combinations to your environment-specific threats helps you stay proactive and make informed decisions with incident response strategies.
Different feeds provide different insights, but before diving deeper into integration, it's important to understand the building blocks themselves: the types of IOCs.
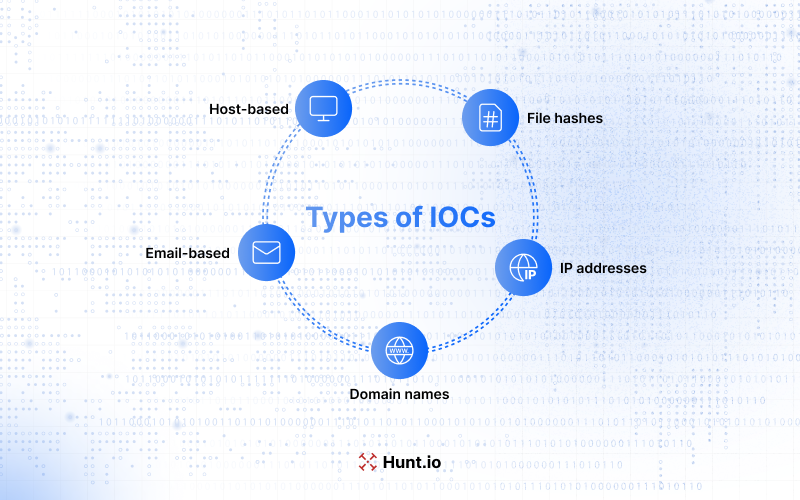
Types of IOCs
Indicators of compromise come in many forms, each highlighting different aspects of potential threats. The main types are:
File hashes: Unique identifiers for files that can reveal malicious executables.
IP addresses: Often point to sources of malicious activity, including known malicious IP addresses.
Domain names: Frequently indicate command-and-control (C2) servers used by attackers.
Email-based: Focus on anomalies in email communications, including phishing attempts and unsolicited attachments.
Host-based: Involve unauthorized file modifications, registry changes, and unexpected process executions, all of which can signal a system compromise.
Understanding these different types of IOCs helps you detect and respond to cyber threats better. And now that we comprehend them, the next question is: how are they shared and distributed across different platforms and tools? That's where formats and protocols come in.
Formats and Protocols for Sharing IOC Feeds
IOC feeds are shared using established formats to ensure compatibility with different security systems. Common formats are:
STIX (Structured Threat Information eXpression): A standardized way to convey threat intelligence, so information sharing is consistent.
TAXII (Trusted Automated eXchange of Indicator Information): A protocol to exchange threat data between different systems.
JSON.
CSV.
Formats like JSON and CSV help integrate IOC data with threat hunting tools by:
Making it easier for you to consume and act on the information.
Helping to organize and distribute threat intelligence efficiently.
Ensuring security teams get accurate and actionable data.
Having standardized formats makes it possible to put these feeds to work, but the real value comes when IOC feeds are integrated with your security tools.
Integrating IOC Feeds with SIEM and EDR Security Tools
Integrating IOC feeds with security tools like SIEM and EDR systems is key to real-time threat detection. These tools aggregate and normalize IOC data so you can distribute it across different security solutions. Continuous monitoring of threat intelligence feeds helps security teams find potential security incidents and respond fast.
Using IOC feeds in intrusion detection systems helps block known malicious traffic automatically, so the overall security posture improves. Combining behavioral analysis with IOC feeds speeds up and improves threat detection, so you can detect and mitigate threats better.
Including entity behavior analytics can further enhance these capabilities. Threat hunting platforms are also key to this integration. They aggregate, normalize, and distribute IOCs. This seamless integration is critical to staying ahead of evolving cyber threats.
Keep in mind that, while integrations are powerful, they only work well if you follow certain best practices.
Best Practices for Using IOC Feeds

Best practices maximize IOC feeds. Key recommendations include:
Using multiple threat intelligence sources to enhance defense by providing different insights into potential threats.
Prioritizing high-confidence IOCs to improve data quality and reduce false positives.
Focusing security teams on the most critical threats.
Updating and cross-checking IOC data regularly is essential to adapt to changing threats and keep threat intelligence relevant.
Using Multiple Threat Intelligence Sources
Gathering indicators from multiple trusted sources helps organizations improve threat remediation and build a stronger cybersecurity framework. Customizing threat feeds to your organization's context can significantly enhance the value of the information.
By using multiple threat intelligence sources, organizations can have a more robust cybersecurity and better defense against security threats. Using diverse and customized threat intelligence strategies helps security teams have access to the most relevant and actionable threat intelligence to respond to threats.
Prioritizing High-Confidence IOCs
Effective IOC feeds should:
Have high-quality data that provides context to help security teams distinguish between real threats and benign activities.
Assess the credibility of feed providers to ensure the threat intelligence is actionable and relevant.
Prioritizing high-confidence IOCs simplifies security and enhances overall defenses.
Updating and Cross-Checking IOC Data Regularly
Updating IOC feeds regularly is essential to staying effective against evolving cyber threats. IOC feeds are more effective when updated to reflect the latest threat landscape.
Updating and cross-checking IOC data is critical to adapt to changing threat environments and keep real-time threat intelligence. IOC feeds are critical to an organization's response throughout the entire cyber attack lifecycle.
For example, sudden traffic spikes indicated by IOC feeds can denote a DDoS attack and trigger immediate defensive actions. Changes to system files and configurations can mean malware, and prompt a quick response to contain and mitigate the threat. Indicators like moving files to unknown directories can mean ongoing data breaches and require immediate investigation.
These examples show how IOC feeds can improve threat detection and mitigation strategies, and give organizations the tools to respond to various emerging cyber threats.
Following these practices helps teams get more from IOC feeds, but theory alone isn't enough; you also need to know where to find the most reliable feeds available today.
Top 7 IOC Feeds to Follow in 2026
In 2026, these IOC feeds stand out for their reliability, coverage, and value to security teams.
1. OpenPhish
OpenPhish focuses on phishing threats and provides a clean, dedicated stream of intelligence. It continuously crawls and verifies phishing URLs with machine learning, which makes it one of the most effective tools for defenders monitoring email and web traffic.
The premium feed supports both CSV and JSON formats, allowing easy integration into SIEMs and email security systems. Many teams use it as their main source for phishing detection because the output is structured, reliable, and quick to update.
2. IOC Hunter Feed
IOC Hunter is different from most feeds. Instead of pushing raw indicators, it extracts them from more than 175 trusted publications, validates them, and enriches them with threat actor details, malware families, and links back to the original source.
The difference is in the context. The IOC Hunter Feed ties every indicator back to the original publication and adds enrichment that makes pivoting faster and easier. Analysts can move from one file hash or domain to related IP addresses, hosting providers, or overlapping malware infrastructure. This is especially valuable for tracking C2 servers and uncovering attacker networks that would otherwise remain hidden.
3. FBI InfraGard
InfraGard is a public-private intelligence-sharing partnership between the FBI and U.S. infrastructure sectors. It delivers industry-specific threat intelligence with direct insight from law enforcement.
It is particularly valuable because the information is tied to critical sectors like energy, healthcare, and IT. Members gain access to early warnings and localized alerts, often before they surface publicly.
4. IBM X-Force Exchange
IBM X-Force Exchange provides a cloud platform for researching and sharing global threat data. It aggregates IOCs from a wide range of sources and integrates with IBM QRadar and other SIEMs.
What sets it apart is its collaborative design. Security teams can create collections, annotate indicators, and plug feeds directly into detection rules to turn intelligence into action.
5. AlienVault Open Threat Exchange (OTX)
.png)
OTX is a community-driven platform that processes millions of indicators each day. Researchers and security teams contribute "pulses" that bundle IOCs with context about campaigns and malware.
Because of the community model, OTX often surfaces indicators within hours of new research being published. It also supports formats like STIX, JSON, CSV, and OpenIoC, making it easy to integrate.
6. LevelBlue Labs

LevelBlue Labs plays a key role in powering OTX with curated IOCs and context on threat actors and targeted industries. Their feed is enriched with additional metadata that strengthens detection.
They also provide coordinated rule updates that can be applied across detection systems. This ensures your defensive tools evolve in sync with new attacker activity.
7. Blocklist.de

Blocklist.de provides IPs associated with brute-force attempts and service-specific attacks such as SSH, mail login, FTP, and web server exploits. It is updated every 12 hours and is widely used as a quick defensive layer.
Its value is in its simplicity. You can drop the feed directly into firewall or proxy configurations to cut down on background noise from opportunistic attacks.
8. TweetFeed
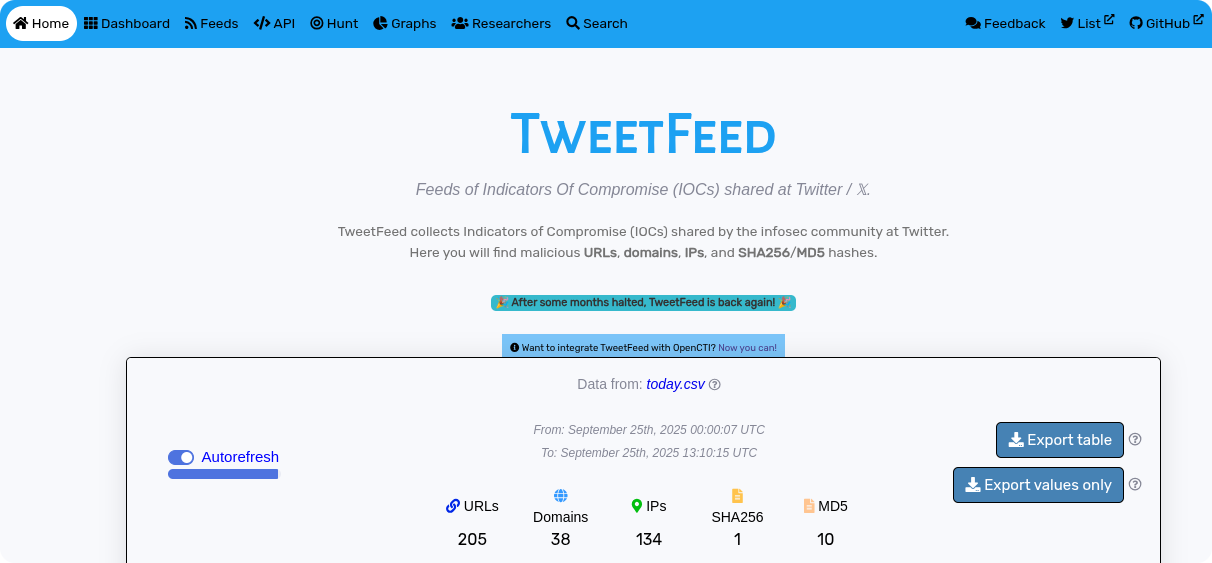
TweetFeed collects IOCs that the infosec community shares on Twitter (X): malicious URLs, domains, IPs, and file hashes (MD5 and SHA‑256) are pulled in near real-time from public tweets.
It's a fast and informal way to stay ahead of raw indicators shared during active campaigns, though confidence varies. That makes it ideal for triage or feeding watchlists rather than outright blocklists.
9. Viriback C2 Tracker
The C2 Tracker GitHub project is a community-driven initiative that uses Shodan-based queries to collect IPs linked to malware, botnets, and C2 infrastructure. The feed updates weekly and comes in plain text format.
Its version history means you can track an IP over time or review when it appeared in the feed. There's even an OpenCTI connector for integration, good for sleuthing infrastructure trends long term.
With so many feeds to choose from, it can be tricky to know which ones to prioritize. That's why the final step is learning how to choose the right feeds for your organization's specific needs.
How to Choose the Right IOC Feeds for Your Organization
Choosing the right IOC feeds for your organization means taking into account your security needs, team size, your threat hunting maturity level, and the type of threats most likely to target your environment. No single feed covers everything, so building the right mix is about striking a balance between breadth and depth.
One of the most important factors is quality. Many feeds push out massive volumes of indicators, but when most of them are low fidelity, it creates more work than value. Analysts end up spending hours curating noisy data and chasing false positives instead of focusing on real threats. This overload is one of the biggest pitfalls of relying on broad, unfiltered feeds.
That is where high-fidelity feeds become critical. Our IOC Hunter Feed is designed to reduce noise by validating and enriching indicators before they ever reach your dashboard. Instead of overwhelming you with endless lists, it focuses on IOCs tied to real malicious campaigns and trusted sources. The result is a feed that helps analysts detect threats and track attacker infrastructure without drowning in false positives.
By prioritizing feeds that deliver accuracy and context, organizations can make their threat hunting program more efficient and actionable, turning raw data into a clear advantage against adversaries.
Now, let's look at a real-life scenario where we used IOC Hunter as a starting point to uncover malicious infrastructure.
Real World Scenario: Starting an Infrastructure Hunt with IOC Hunter
In this investigation, which was published in our blog back in March under the title A Practical Guide to Uncovering Malicious Infrastructure With Hunt.io, the starting point was an indicator from our IOC Hunter feed, which provided an IP address tied to suspicious activity.
Based on this indicator, analysts began by querying the IP to uncover hosting details, domains, and open ports. The IP was linked to BL Networks, a VPS provider often used by cybercriminals, and associated with a cryptocurrency fraud-related domain.

From there, the hunt expanded into service analysis and TLS certificate history. Ports 22, 80, and 443 revealed generic responses, but a self-signed TLS certificate with a unique JA4X hash provided a strong pivot point. Querying Hunt's dataset showed only a handful of servers sharing this fingerprint, suggesting a small cluster of related infrastructure.
Cross-referencing with external sources like VirusTotal hinted at a possible connection to Latrodectus malware. While not every lead confirmed attribution, the process demonstrates how starting with a single IOC, validated and enriched through IOC Hunter, can uncover hidden infrastructure and strengthen defender awareness of attacker operations.
Conclusion
IOC feeds remain a practical way to keep pace with evolving threats, but their value lies in choosing wisely. Free and community-driven options cast a wide net, while high-fidelity feeds like our IOC Hunter Feed deliver accuracy and enrichment to track malicious campaigns without wasting analyst hours. Combining feeds on phishing, brute-force, malware, and attribution gives your team a clearer picture of adversary behavior.
Ready to see how high-fidelity IOCs can uncover hidden infrastructure and keep you ahead of campaigns? Our team can show you. Book a demo now!
IOC feeds provide real-time data to spot and counter cyber threats. But keeping up with this flood of information is no small task; in fact, the average security analyst spends 2-4 hours every day sifting through threat intelligence, according to market.us.
And the pressure is only growing: the Identity Theft Resource Center (ITRC) reported 1,732 data compromises in just the first half of 2026, impacting nearly 166 million people.
With the right IOC feeds, however, you can cut through the noise, act faster, and strengthen your defenses.
That's why in this article, we'll walk through the top 10 IOC feeds for 2026, explain their role in threat detection, and help you choose the ones that deliver the most impact for your cybersecurity strategy.
The Basics: What are IOC Feeds?
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) are forensic artifacts that signal potential network breaches or intrusions. Microsoft defines them as "evidence that someone may have breached an organization's network or endpoint."

These artifacts are warning signs, alerting security teams regarding malicious activity that could compromise system integrity. Using them effectively is key to proactive defense and rapid incident response, so you can detect breaches in days, not weeks.
IOC feeds are streams of data that provide real-time information about potential threats. This continuous flow of threat-related data helps you tackle cybercriminals by identifying and mitigating threats at different stages of the attack lifecycle, from reconnaissance to exploitation. Monitoring these feeds helps with proactive threat hunting, so security teams can find advanced threats before they cause damage.
Analyzing IOCs regularly helps you find security gaps and refine your defenses. This not only improves your overall security but also helps with compliance. Tangible evidence provided by IOCs like malicious IP addresses or unusual login attempts is gold in incident detection and response.
Now that we've covered what IOC feeds are and why they matter, let's look at why relying on just one feed isn't enough.
Why You Need More Than One IOC Feed
Using multiple IOC feeds is essential to get a full picture of the threat landscape. Different feeds have different data collection methods, so they provide different insights that enhance overall threat detection. This diversity helps prevent data gaps, so you're not relying on a single source for threat intelligence.
Including multiple feeds allows for cross-referencing of information, which validates indicators and makes the data more relevant. This helps security teams prioritize threats so they can respond faster and more effectively to potential threats. Customizing IOC feed combinations to your environment-specific threats helps you stay proactive and make informed decisions with incident response strategies.
Different feeds provide different insights, but before diving deeper into integration, it's important to understand the building blocks themselves: the types of IOCs.
Types of IOCs
Indicators of compromise come in many forms, each highlighting different aspects of potential threats. The main types are:
File hashes: Unique identifiers for files that can reveal malicious executables.
IP addresses: Often point to sources of malicious activity, including known malicious IP addresses.
Domain names: Frequently indicate command-and-control (C2) servers used by attackers.
Email-based: Focus on anomalies in email communications, including phishing attempts and unsolicited attachments.
Host-based: Involve unauthorized file modifications, registry changes, and unexpected process executions, all of which can signal a system compromise.
Understanding these different types of IOCs helps you detect and respond to cyber threats better. And now that we comprehend them, the next question is: how are they shared and distributed across different platforms and tools? That's where formats and protocols come in.

Formats and Protocols for Sharing IOC Feeds
IOC feeds are shared using established formats to ensure compatibility with different security systems. Common formats are:
STIX (Structured Threat Information eXpression): A standardized way to convey threat intelligence, so information sharing is consistent.
TAXII (Trusted Automated eXchange of Indicator Information): A protocol to exchange threat data between different systems.
JSON.
CSV.
Formats like JSON and CSV help integrate IOC data with threat hunting tools by:
Making it easier for you to consume and act on the information.
Helping to organize and distribute threat intelligence efficiently.
Ensuring security teams get accurate and actionable data.
Having standardized formats makes it possible to put these feeds to work, but the real value comes when IOC feeds are integrated with your security tools.
Integrating IOC Feeds with SIEM and EDR Security Tools
Integrating IOC feeds with security tools like SIEM and EDR systems is key to real-time threat detection. These tools aggregate and normalize IOC data so you can distribute it across different security solutions. Continuous monitoring of threat intelligence feeds helps security teams find potential security incidents and respond fast.
Using IOC feeds in intrusion detection systems helps block known malicious traffic automatically, so the overall security posture improves. Combining behavioral analysis with IOC feeds speeds up and improves threat detection, so you can detect and mitigate threats better.
Including entity behavior analytics can further enhance these capabilities. Threat hunting platforms are also key to this integration. They aggregate, normalize, and distribute IOCs. This seamless integration is critical to staying ahead of evolving cyber threats.
Keep in mind that, while integrations are powerful, they only work well if you follow certain best practices.
Best Practices for Using IOC Feeds

Best practices maximize IOC feeds. Key recommendations include:
Using multiple threat intelligence sources to enhance defense by providing different insights into potential threats.
Prioritizing high-confidence IOCs to improve data quality and reduce false positives.
Focusing security teams on the most critical threats.
Updating and cross-checking IOC data regularly is essential to adapt to changing threats and keep threat intelligence relevant.
Using Multiple Threat Intelligence Sources
Gathering indicators from multiple trusted sources helps organizations improve threat remediation and build a stronger cybersecurity framework. Customizing threat feeds to your organization's context can significantly enhance the value of the information.
By using multiple threat intelligence sources, organizations can have a more robust cybersecurity and better defense against security threats. Using diverse and customized threat intelligence strategies helps security teams have access to the most relevant and actionable threat intelligence to respond to threats.
Prioritizing High-Confidence IOCs
Effective IOC feeds should:
Have high-quality data that provides context to help security teams distinguish between real threats and benign activities.
Assess the credibility of feed providers to ensure the threat intelligence is actionable and relevant.
Prioritizing high-confidence IOCs simplifies security and enhances overall defenses.
Updating and Cross-Checking IOC Data Regularly
Updating IOC feeds regularly is essential to staying effective against evolving cyber threats. IOC feeds are more effective when updated to reflect the latest threat landscape.
Updating and cross-checking IOC data is critical to adapt to changing threat environments and keep real-time threat intelligence. IOC feeds are critical to an organization's response throughout the entire cyber attack lifecycle.
For example, sudden traffic spikes indicated by IOC feeds can denote a DDoS attack and trigger immediate defensive actions. Changes to system files and configurations can mean malware, and prompt a quick response to contain and mitigate the threat. Indicators like moving files to unknown directories can mean ongoing data breaches and require immediate investigation.
These examples show how IOC feeds can improve threat detection and mitigation strategies, and give organizations the tools to respond to various emerging cyber threats.
Following these practices helps teams get more from IOC feeds, but theory alone isn't enough; you also need to know where to find the most reliable feeds available today.
Top 7 IOC Feeds to Follow in 2026
In 2026, these IOC feeds stand out for their reliability, coverage, and value to security teams.
1. OpenPhish

OpenPhish focuses on phishing threats and provides a clean, dedicated stream of intelligence. It continuously crawls and verifies phishing URLs with machine learning, which makes it one of the most effective tools for defenders monitoring email and web traffic.
The premium feed supports both CSV and JSON formats, allowing easy integration into SIEMs and email security systems. Many teams use it as their main source for phishing detection because the output is structured, reliable, and quick to update.
2. IOC Hunter Feed

IOC Hunter is different from most feeds. Instead of pushing raw indicators, it extracts them from more than 175 trusted publications, validates them, and enriches them with threat actor details, malware families, and links back to the original source.
The difference is in the context. The IOC Hunter Feed ties every indicator back to the original publication and adds enrichment that makes pivoting faster and easier. Analysts can move from one file hash or domain to related IP addresses, hosting providers, or overlapping malware infrastructure. This is especially valuable for tracking C2 servers and uncovering attacker networks that would otherwise remain hidden.
3. FBI InfraGard

InfraGard is a public-private intelligence-sharing partnership between the FBI and U.S. infrastructure sectors. It delivers industry-specific threat intelligence with direct insight from law enforcement.
It is particularly valuable because the information is tied to critical sectors like energy, healthcare, and IT. Members gain access to early warnings and localized alerts, often before they surface publicly.
4. IBM X-Force Exchange

IBM X-Force Exchange provides a cloud platform for researching and sharing global threat data. It aggregates IOCs from a wide range of sources and integrates with IBM QRadar and other SIEMs.
What sets it apart is its collaborative design. Security teams can create collections, annotate indicators, and plug feeds directly into detection rules to turn intelligence into action.
5. AlienVault Open Threat Exchange (OTX)
.png)
OTX is a community-driven platform that processes millions of indicators each day. Researchers and security teams contribute "pulses" that bundle IOCs with context about campaigns and malware.
Because of the community model, OTX often surfaces indicators within hours of new research being published. It also supports formats like STIX, JSON, CSV, and OpenIoC, making it easy to integrate.
6. LevelBlue Labs

LevelBlue Labs plays a key role in powering OTX with curated IOCs and context on threat actors and targeted industries. Their feed is enriched with additional metadata that strengthens detection.
They also provide coordinated rule updates that can be applied across detection systems. This ensures your defensive tools evolve in sync with new attacker activity.
7. Blocklist.de

Blocklist.de provides IPs associated with brute-force attempts and service-specific attacks such as SSH, mail login, FTP, and web server exploits. It is updated every 12 hours and is widely used as a quick defensive layer.
Its value is in its simplicity. You can drop the feed directly into firewall or proxy configurations to cut down on background noise from opportunistic attacks.
8. TweetFeed

TweetFeed collects IOCs that the infosec community shares on Twitter (X): malicious URLs, domains, IPs, and file hashes (MD5 and SHA‑256) are pulled in near real-time from public tweets.
It's a fast and informal way to stay ahead of raw indicators shared during active campaigns, though confidence varies. That makes it ideal for triage or feeding watchlists rather than outright blocklists.
9. Viriback C2 Tracker
The C2 Tracker GitHub project is a community-driven initiative that uses Shodan-based queries to collect IPs linked to malware, botnets, and C2 infrastructure. The feed updates weekly and comes in plain text format.
Its version history means you can track an IP over time or review when it appeared in the feed. There's even an OpenCTI connector for integration, good for sleuthing infrastructure trends long term.
With so many feeds to choose from, it can be tricky to know which ones to prioritize. That's why the final step is learning how to choose the right feeds for your organization's specific needs.
How to Choose the Right IOC Feeds for Your Organization
Choosing the right IOC feeds for your organization means taking into account your security needs, team size, your threat hunting maturity level, and the type of threats most likely to target your environment. No single feed covers everything, so building the right mix is about striking a balance between breadth and depth.
One of the most important factors is quality. Many feeds push out massive volumes of indicators, but when most of them are low fidelity, it creates more work than value. Analysts end up spending hours curating noisy data and chasing false positives instead of focusing on real threats. This overload is one of the biggest pitfalls of relying on broad, unfiltered feeds.
That is where high-fidelity feeds become critical. Our IOC Hunter Feed is designed to reduce noise by validating and enriching indicators before they ever reach your dashboard. Instead of overwhelming you with endless lists, it focuses on IOCs tied to real malicious campaigns and trusted sources. The result is a feed that helps analysts detect threats and track attacker infrastructure without drowning in false positives.
By prioritizing feeds that deliver accuracy and context, organizations can make their threat hunting program more efficient and actionable, turning raw data into a clear advantage against adversaries.
Now, let's look at a real-life scenario where we used IOC Hunter as a starting point to uncover malicious infrastructure.
Real World Scenario: Starting an Infrastructure Hunt with IOC Hunter
In this investigation, which was published in our blog back in March under the title A Practical Guide to Uncovering Malicious Infrastructure With Hunt.io, the starting point was an indicator from our IOC Hunter feed, which provided an IP address tied to suspicious activity.
Based on this indicator, analysts began by querying the IP to uncover hosting details, domains, and open ports. The IP was linked to BL Networks, a VPS provider often used by cybercriminals, and associated with a cryptocurrency fraud-related domain.

From there, the hunt expanded into service analysis and TLS certificate history. Ports 22, 80, and 443 revealed generic responses, but a self-signed TLS certificate with a unique JA4X hash provided a strong pivot point. Querying Hunt's dataset showed only a handful of servers sharing this fingerprint, suggesting a small cluster of related infrastructure.
Cross-referencing with external sources like VirusTotal hinted at a possible connection to Latrodectus malware. While not every lead confirmed attribution, the process demonstrates how starting with a single IOC, validated and enriched through IOC Hunter, can uncover hidden infrastructure and strengthen defender awareness of attacker operations.
Conclusion
IOC feeds remain a practical way to keep pace with evolving threats, but their value lies in choosing wisely. Free and community-driven options cast a wide net, while high-fidelity feeds like our IOC Hunter Feed deliver accuracy and enrichment to track malicious campaigns without wasting analyst hours. Combining feeds on phishing, brute-force, malware, and attribution gives your team a clearer picture of adversary behavior.
Ready to see how high-fidelity IOCs can uncover hidden infrastructure and keep you ahead of campaigns? Our team can show you. Book a demo now!
Related Posts
Related Posts
Related Posts
Hunt adversary infrastructure in real time. Surface C2 servers, enrich IOCs,
and map attacker activity at scale with our unified threat hunting platform.

Hunt adversary infrastructure in real time. Surface C2 servers, enrich IOCs,
and map attacker activity at scale with our unified threat hunting platform.

Hunt adversary infrastructure in real time. Surface C2 servers, enrich IOCs,
and map attacker activity at scale with our unified threat hunting platform.






