Threat Hunting Maturity Model: A Practical Guide
Published on Oct 23, 2025
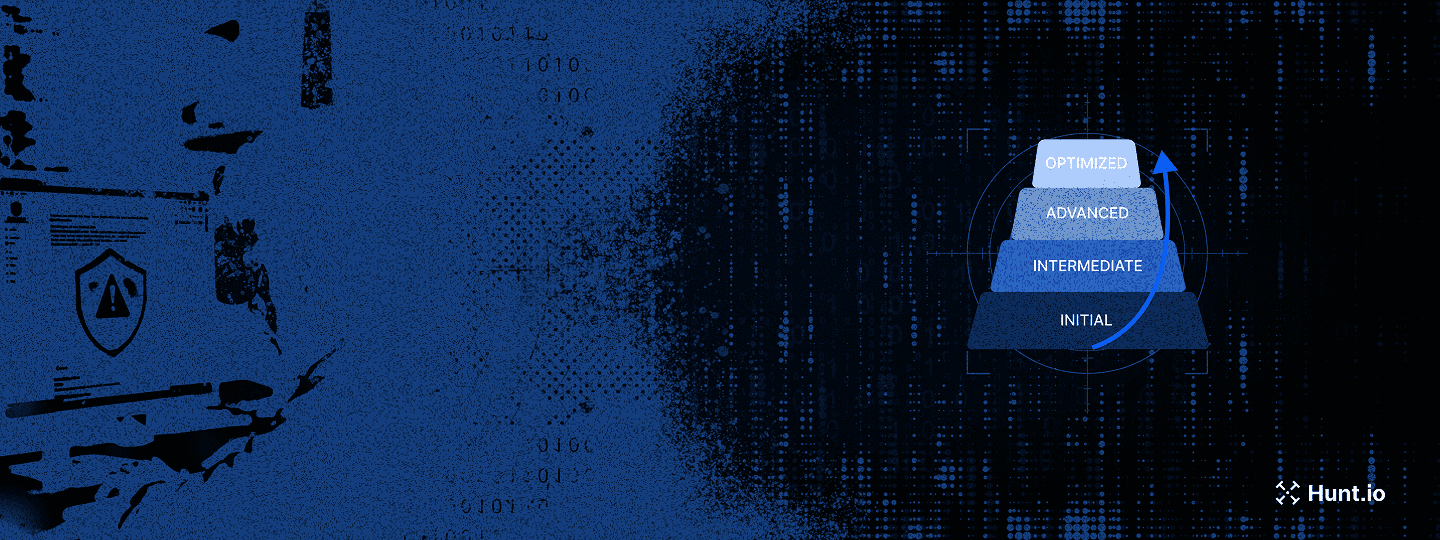
The Threat Hunting Maturity Model (HMM) is a framework that helps organizations improve their threat hunting skills and strengthen their defenses against evolving cyber threats. These threats are growing more complex every year, and organizations are under increasing pressure to stay ahead of attackers.
The FBI's 2024 Internet Crime Report (published in April 2025) highlights the scale of the problem, with over 800,000 complaints of suspected internet crime and losses exceeding $16 billion, which marks a 33% increase from 2023. It's no surprise then that the threat hunting market is projected to reach a value of $6.9 billion by 2029 as businesses invest heavily in proactive defenses.
And this is where the Threat Hunting Maturity Model (HMM) comes in. In this article, we'll walk through each level of the model and show how progressing through them can help you detect and respond to threats more effectively, reducing the likelihood of becoming part of those growing crime statistics.
Key Points
The Threat Hunting Maturity Model (HMM) provides a structured framework for organizations to assess and improve their threat hunting capabilities to improve security.
Organizations move through 5 levels, from a reactive approach relying on automated alerts to a proactive approach using advanced analytics and automation for threat detection.
Implementing HMM involves assessing current capabilities, creating a clear roadmap for improvement, and using technology to automate processes to improve incident response and reduce false positives.
What is the Threat Hunting Maturity Model?
The Threat Hunting Maturity Model (HMM) is a must-have for organizations looking to assess and improve their cyber threat hunting capabilities. The SANS Institute defines it as "a simple model for evaluating an organization's threat hunting capability."
Developed by David J. Bianco, HMM provides a structured framework to help organizations understand their current threat hunting skills and identify areas for improvement, bolstering their threat hunting process.
Using HMM allows them to determine their current threat hunting maturity and create a clear roadmap for their hunt team to advance. Moving through it gives you better threat detection and response capabilities, which overall improves your security posture.
This structured approach helps you identify current weaknesses and plan for future improvements. Understanding HMM is the first step to a more secure and proactive security strategy.

HMM Level 0: Initial Stage
At HMM Level 0, you are at the initial level of threat hunting maturity. This stage is characterized by a heavy reliance on automated alerts from systems like antivirus software, Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), and monitoring systems.
You have minimal data collection, a low visibility of your environment, and limited insight into what's going on. At this level, the focus is on reactive detection; the human element is mainly around resolving alerts from automated systems and getting alert resolution.
Organizations at this stage use indicators from open-source services for threat intelligence, but don't have regular data collection practices. The reliance on automated detection systems limits their ability to detect and respond to more advanced threats.
HMM Level 1: Minimal Stage
Moving to HMM Level 1, organizations start to improve their threat hunting by using automated alerting for incident response. At this minimal level, organizations can do some form of threat hunting because they have improved search capability within SIEM platforms. This stage is an improvement in visibility as organizations collect more logs and have a better understanding of their environment.
Effective threat hunting at this level requires as much data and as many types of data as possible. The increased visibility and data collection allow organizations to hunt more reliably and effectively, but they still rely on automated systems for initial detection.
HMM Level 2: Procedural Stage
HMM Level 2 is the procedural stage; this is the most common level of threat hunting maturity among organizations. At this stage, organizations have predefined threat hunting procedures that integrate analytical techniques with specific input data. These procedures are developed by others, and organizations at this level only modify existing threat hunting techniques.
The limitation at this stage is the inability to create new hunting procedures from scratch. Instead, organizations rely on existing processes and techniques, which can limit their ability to innovate and adapt to new threats.
Despite these limitations, the procedural level is a big step forward in terms of structured and repeatable processes for threat hunting, iteratively searching for the same processes to improve their hunting team. Also, these procedures rely on the same foundation principles to ensure consistency and reliability.
HMM Level 3: Innovative Stage
At HMM Level 3, organizations enter the innovative stage where they begin to create their hunting techniques to detect threats, starting to reach an advanced threat hunting level. At this level, threat hunters should have a good understanding of various data analysis methods, which significantly improves threat detection.
This innovative approach allows organizations to stay ahead of advanced threats by making extensive use of threat hunting frameworks, relying on different types of threat hunting, and creating custom and tailored hunting techniques.
But organizations at this level may face challenges related to scalability and the overwhelming number of procedures as their hunting processes grow. Despite these challenges, the innovative level is a high level of maturity in threat hunting.
HMM Level 4: Leading Stage
HMM Level 4 is the leading stage, where automation is high in successful hunting processes. This level is different from the innovative stage by having much higher automation of hunting techniques, so analysts can focus on strategic improvements and overall security posture.
Organizations at this level are very good at stopping notorious adversaries by automating their threat hunting. The high automation allows these mature organizations to focus on more complex and strategic aspects of cybersecurity and have a strong defense against advanced threats.

Understanding the different levels of the HMM gives organizations a clear picture of where they stand today, but to move forward, we need to understand what makes the model work in practice, and that's where the key components come in.
Key Components of the Hunting Maturity Model
Evaluating an organization's threat hunting maturity involves looking at processes, data quality, and response strategies. Reviewing current processes and data analytics practices gives organizations a clear understanding of their current threat hunting capabilities.
Aligning threat hunting practices with the maturity model is key to efficiency and effectiveness. Having a clear roadmap that takes into account current maturity and future goals allows organizations to improve their threat hunting capabilities systematically and ultimately get to a more secure and resilient cybersecurity posture.
Data Collection and Quality
High-quality data is the foundation of effective threat hunting. Accurate analysis and informed decision-making rely on the quality of the data collected. Organizations must collect data from multiple sources, including threat intelligence feeds and internal logs, to have comprehensive coverage of potential threats.
Regular collection and correlation of different types of data is key to uncovering hidden threats. Techniques like data correlation and correlative rules help to link disparate data points and give a clearer picture of security incidents.
As organizations move through the HMM levels, data collection becomes a critical component of improving their threat hunting maturity.
Advanced Data Analysis Techniques
Different maturity levels use different analytical methods to detect and respond to threats. Techniques like clustering, statistical analytics, and machine learning are used to improve threat detection. At higher maturity levels, threat hunters use advanced methods like linked data analysis and data visualization to get deeper insights into potential threats.
Incorporating a powerful threat hunting platform, advanced technologies, and automated tools makes threat hunting more efficient and accurate. Automation can streamline data analysis, alert management, and reduce manual processes. By using machine learning and other advanced technologies, organizations can get to higher maturity levels and improve their overall threat detection and response.
Incorporating threat intelligence feeds into the threat hunting process gives organizations context and insights into potential threats. Threat intelligence makes hunting more effective by providing actionable information on attack vectors, actor behavior, and potential vulnerabilities.
By using threat intelligence indicators and KPIs, organizations can sharpen their detection and improve their response. To stay ahead of evolving threats requires continuous updates from threat feeds and other intelligence sources. This proactive approach allows organizations to detect and isolate advanced threats better and have a strong security posture.
By focusing on processes, data quality, and advanced analysis techniques, organizations can gradually strengthen their hunting capabilities. These components aren't just theoretical; they directly translate into measurable improvements, so let's explore the concrete benefits that come from advancing through the HMM levels.
Benefits of Moving Up the HMM Levels
Moving up the HMM levels brings many benefits to organizations, including better threat detection and response. Proactive threat hunters are an early warning system, identifying potential threats before they escalate. This proactive approach allows organizations to respond to incidents faster and better.
At higher maturity levels, automation plays a big role in freeing analysts from repetitive tasks so they can focus on strategic improvements and more complex threat analysis. This shift to automation and strategic focus not only improves overall security posture but also allows organizations to stay ahead of emerging threats.
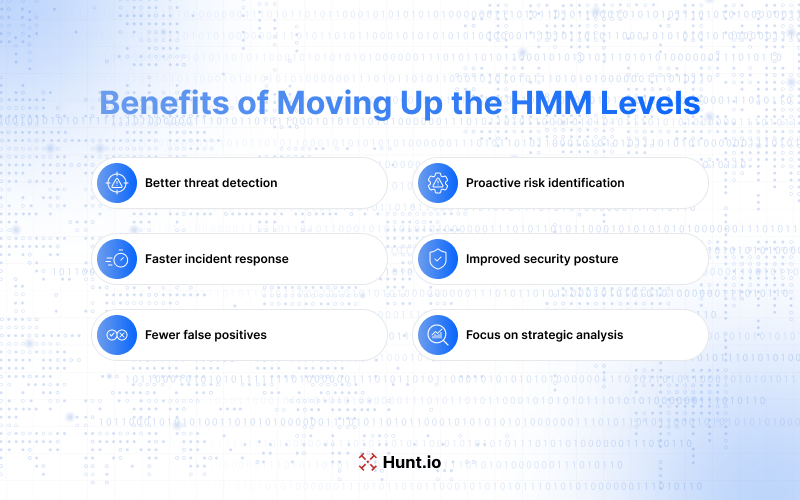
Better Detection
Organizations at higher maturity levels use advanced data analysis techniques, including statistical and machine learning, to improve their threat detection. These advanced techniques allow organizations to detect and prioritize threats based on data patterns and uncover hidden threats that automated systems may miss.
Mature threat hunting allows organizations to detect subtle indicators of compromise (IOCs) that may not be detected by less mature processes. By moving up the HMM, organizations can use advanced techniques to detect potential threats and overall security posture.
Improved Incident Response
A mature threat hunting process allows organizations to respond faster and better to incidents and reduce the time required to mitigate threats. This improved incident response allows teams to detect, contain, and neutralize threats and minimize damage from cyber attacks.
Reviewing current threat hunting practices helps organizations identify strengths and weaknesses and streamline their incident response workflow.
Fewer False Positives
A big challenge for analysts in reactive threat hunting is the high number of false positive alerts related to malicious activity. Higher maturity levels in threat hunting mean better detection accuracy, which minimizes false positive alerts. This allows analysts to detect malicious activity and focus on real threats instead of wasting time on false alarms.
As organizations move up the maturity levels, they can refine detection techniques and reduce false alarms during threat assessments. This reduction in false positives not only improves threat hunting efficiency but also the overall security posture by ensuring resources are allocated to real threats.
Knowing the benefits of higher maturity is motivating, but turning that knowledge into action requires a clear path, so the next step is learning how to implement the Threat Hunting Maturity Model effectively.
How to Implement the Threat Hunting Maturity Model
Successfully implementing the Threat Hunting Maturity Model requires a clear understanding of current capabilities and a defined strategy for progression. Assessing data quality and quantity, data analysis capabilities, and automated analytics are key to determining an organization's current maturity level.
Organizations should create a structured plan to move up the maturity levels by leveraging their capabilities and addressing weaknesses. Having a roadmap for ongoing improvement in threat detection and response is key to achieving higher threat hunting maturity.

Current Maturity Level Assessment
Organizations can assess their maturity level in threat hunting by evaluating their threat hunting process. This is done by comparing current capabilities to the Threat Hunting Maturity Model to identify skill development needs and opportunities for improvement.
Defining opportunities for improvement is key to advancing threat hunting processes and addressing current capability gaps. Knowing their current maturity level allows organizations to create targeted strategies to improve their threat hunting capabilities.
Roadmap for Improvement
Creating a roadmap involves identifying specific milestones and timelines to move up the threat hunting maturity levels. This often involves setting specific milestones and prioritizing actions that align with the organization's threat hunting strategy.
A clear roadmap should have specific milestones and measurable goals to track progress in improving threat hunting capabilities regularly. This structured improvement plan allows organizations to move up the maturity levels and achieve their cybersecurity goals.
Technology and Automation
Organizations at the innovative stage develop custom data analysis techniques and have skilled threat hunters to isolate advanced threats. Leveraging technology and automation is key to moving up the Threat Hunting Maturity Model to detect and respond to sophisticated threats.
The leading stage has high automation of successful hunting processes, so analysts can focus on strategic improvements and overall security posture. Using advanced data analysis techniques and automated detection systems reduces false positives and improves threat detection accuracy.
Conclusion
The Threat Hunting Maturity Model is more than a framework; it's a roadmap to stronger, proactive security. By assessing your current level and advancing through the stages, you can reduce risks, improve detection, and respond faster. With the right tools, threat hunting becomes easier and more effective.
Ready to see it in action? Book a demo now and discover how our platform can help you advance through the HMM levels and build a stronger, more proactive security posture.
The Threat Hunting Maturity Model (HMM) is a framework that helps organizations improve their threat hunting skills and strengthen their defenses against evolving cyber threats. These threats are growing more complex every year, and organizations are under increasing pressure to stay ahead of attackers.
The FBI's 2024 Internet Crime Report (published in April 2025) highlights the scale of the problem, with over 800,000 complaints of suspected internet crime and losses exceeding $16 billion, which marks a 33% increase from 2023. It's no surprise then that the threat hunting market is projected to reach a value of $6.9 billion by 2029 as businesses invest heavily in proactive defenses.
And this is where the Threat Hunting Maturity Model (HMM) comes in. In this article, we'll walk through each level of the model and show how progressing through them can help you detect and respond to threats more effectively, reducing the likelihood of becoming part of those growing crime statistics.
Key Points
The Threat Hunting Maturity Model (HMM) provides a structured framework for organizations to assess and improve their threat hunting capabilities to improve security.
Organizations move through 5 levels, from a reactive approach relying on automated alerts to a proactive approach using advanced analytics and automation for threat detection.
Implementing HMM involves assessing current capabilities, creating a clear roadmap for improvement, and using technology to automate processes to improve incident response and reduce false positives.
What is the Threat Hunting Maturity Model?
The Threat Hunting Maturity Model (HMM) is a must-have for organizations looking to assess and improve their cyber threat hunting capabilities. The SANS Institute defines it as "a simple model for evaluating an organization's threat hunting capability."
Developed by David J. Bianco, HMM provides a structured framework to help organizations understand their current threat hunting skills and identify areas for improvement, bolstering their threat hunting process.
Using HMM allows them to determine their current threat hunting maturity and create a clear roadmap for their hunt team to advance. Moving through it gives you better threat detection and response capabilities, which overall improves your security posture.
This structured approach helps you identify current weaknesses and plan for future improvements. Understanding HMM is the first step to a more secure and proactive security strategy.

HMM Level 0: Initial Stage
At HMM Level 0, you are at the initial level of threat hunting maturity. This stage is characterized by a heavy reliance on automated alerts from systems like antivirus software, Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), and monitoring systems.
You have minimal data collection, a low visibility of your environment, and limited insight into what's going on. At this level, the focus is on reactive detection; the human element is mainly around resolving alerts from automated systems and getting alert resolution.
Organizations at this stage use indicators from open-source services for threat intelligence, but don't have regular data collection practices. The reliance on automated detection systems limits their ability to detect and respond to more advanced threats.
HMM Level 1: Minimal Stage
Moving to HMM Level 1, organizations start to improve their threat hunting by using automated alerting for incident response. At this minimal level, organizations can do some form of threat hunting because they have improved search capability within SIEM platforms. This stage is an improvement in visibility as organizations collect more logs and have a better understanding of their environment.
Effective threat hunting at this level requires as much data and as many types of data as possible. The increased visibility and data collection allow organizations to hunt more reliably and effectively, but they still rely on automated systems for initial detection.
HMM Level 2: Procedural Stage
HMM Level 2 is the procedural stage; this is the most common level of threat hunting maturity among organizations. At this stage, organizations have predefined threat hunting procedures that integrate analytical techniques with specific input data. These procedures are developed by others, and organizations at this level only modify existing threat hunting techniques.
The limitation at this stage is the inability to create new hunting procedures from scratch. Instead, organizations rely on existing processes and techniques, which can limit their ability to innovate and adapt to new threats.
Despite these limitations, the procedural level is a big step forward in terms of structured and repeatable processes for threat hunting, iteratively searching for the same processes to improve their hunting team. Also, these procedures rely on the same foundation principles to ensure consistency and reliability.
HMM Level 3: Innovative Stage
At HMM Level 3, organizations enter the innovative stage where they begin to create their hunting techniques to detect threats, starting to reach an advanced threat hunting level. At this level, threat hunters should have a good understanding of various data analysis methods, which significantly improves threat detection.
This innovative approach allows organizations to stay ahead of advanced threats by making extensive use of threat hunting frameworks, relying on different types of threat hunting, and creating custom and tailored hunting techniques.
But organizations at this level may face challenges related to scalability and the overwhelming number of procedures as their hunting processes grow. Despite these challenges, the innovative level is a high level of maturity in threat hunting.
HMM Level 4: Leading Stage
HMM Level 4 is the leading stage, where automation is high in successful hunting processes. This level is different from the innovative stage by having much higher automation of hunting techniques, so analysts can focus on strategic improvements and overall security posture.
Organizations at this level are very good at stopping notorious adversaries by automating their threat hunting. The high automation allows these mature organizations to focus on more complex and strategic aspects of cybersecurity and have a strong defense against advanced threats.

Understanding the different levels of the HMM gives organizations a clear picture of where they stand today, but to move forward, we need to understand what makes the model work in practice, and that's where the key components come in.
Key Components of the Hunting Maturity Model
Evaluating an organization's threat hunting maturity involves looking at processes, data quality, and response strategies. Reviewing current processes and data analytics practices gives organizations a clear understanding of their current threat hunting capabilities.
Aligning threat hunting practices with the maturity model is key to efficiency and effectiveness. Having a clear roadmap that takes into account current maturity and future goals allows organizations to improve their threat hunting capabilities systematically and ultimately get to a more secure and resilient cybersecurity posture.
Data Collection and Quality
High-quality data is the foundation of effective threat hunting. Accurate analysis and informed decision-making rely on the quality of the data collected. Organizations must collect data from multiple sources, including threat intelligence feeds and internal logs, to have comprehensive coverage of potential threats.
Regular collection and correlation of different types of data is key to uncovering hidden threats. Techniques like data correlation and correlative rules help to link disparate data points and give a clearer picture of security incidents.
As organizations move through the HMM levels, data collection becomes a critical component of improving their threat hunting maturity.
Advanced Data Analysis Techniques
Different maturity levels use different analytical methods to detect and respond to threats. Techniques like clustering, statistical analytics, and machine learning are used to improve threat detection. At higher maturity levels, threat hunters use advanced methods like linked data analysis and data visualization to get deeper insights into potential threats.
Incorporating a powerful threat hunting platform, advanced technologies, and automated tools makes threat hunting more efficient and accurate. Automation can streamline data analysis, alert management, and reduce manual processes. By using machine learning and other advanced technologies, organizations can get to higher maturity levels and improve their overall threat detection and response.
Incorporating threat intelligence feeds into the threat hunting process gives organizations context and insights into potential threats. Threat intelligence makes hunting more effective by providing actionable information on attack vectors, actor behavior, and potential vulnerabilities.
By using threat intelligence indicators and KPIs, organizations can sharpen their detection and improve their response. To stay ahead of evolving threats requires continuous updates from threat feeds and other intelligence sources. This proactive approach allows organizations to detect and isolate advanced threats better and have a strong security posture.
By focusing on processes, data quality, and advanced analysis techniques, organizations can gradually strengthen their hunting capabilities. These components aren't just theoretical; they directly translate into measurable improvements, so let's explore the concrete benefits that come from advancing through the HMM levels.
Benefits of Moving Up the HMM Levels
Moving up the HMM levels brings many benefits to organizations, including better threat detection and response. Proactive threat hunters are an early warning system, identifying potential threats before they escalate. This proactive approach allows organizations to respond to incidents faster and better.
At higher maturity levels, automation plays a big role in freeing analysts from repetitive tasks so they can focus on strategic improvements and more complex threat analysis. This shift to automation and strategic focus not only improves overall security posture but also allows organizations to stay ahead of emerging threats.

Better Detection
Organizations at higher maturity levels use advanced data analysis techniques, including statistical and machine learning, to improve their threat detection. These advanced techniques allow organizations to detect and prioritize threats based on data patterns and uncover hidden threats that automated systems may miss.
Mature threat hunting allows organizations to detect subtle indicators of compromise (IOCs) that may not be detected by less mature processes. By moving up the HMM, organizations can use advanced techniques to detect potential threats and overall security posture.
Improved Incident Response
A mature threat hunting process allows organizations to respond faster and better to incidents and reduce the time required to mitigate threats. This improved incident response allows teams to detect, contain, and neutralize threats and minimize damage from cyber attacks.
Reviewing current threat hunting practices helps organizations identify strengths and weaknesses and streamline their incident response workflow.
Fewer False Positives
A big challenge for analysts in reactive threat hunting is the high number of false positive alerts related to malicious activity. Higher maturity levels in threat hunting mean better detection accuracy, which minimizes false positive alerts. This allows analysts to detect malicious activity and focus on real threats instead of wasting time on false alarms.
As organizations move up the maturity levels, they can refine detection techniques and reduce false alarms during threat assessments. This reduction in false positives not only improves threat hunting efficiency but also the overall security posture by ensuring resources are allocated to real threats.
Knowing the benefits of higher maturity is motivating, but turning that knowledge into action requires a clear path, so the next step is learning how to implement the Threat Hunting Maturity Model effectively.
How to Implement the Threat Hunting Maturity Model
Successfully implementing the Threat Hunting Maturity Model requires a clear understanding of current capabilities and a defined strategy for progression. Assessing data quality and quantity, data analysis capabilities, and automated analytics are key to determining an organization's current maturity level.
Organizations should create a structured plan to move up the maturity levels by leveraging their capabilities and addressing weaknesses. Having a roadmap for ongoing improvement in threat detection and response is key to achieving higher threat hunting maturity.

Current Maturity Level Assessment
Organizations can assess their maturity level in threat hunting by evaluating their threat hunting process. This is done by comparing current capabilities to the Threat Hunting Maturity Model to identify skill development needs and opportunities for improvement.
Defining opportunities for improvement is key to advancing threat hunting processes and addressing current capability gaps. Knowing their current maturity level allows organizations to create targeted strategies to improve their threat hunting capabilities.
Roadmap for Improvement
Creating a roadmap involves identifying specific milestones and timelines to move up the threat hunting maturity levels. This often involves setting specific milestones and prioritizing actions that align with the organization's threat hunting strategy.
A clear roadmap should have specific milestones and measurable goals to track progress in improving threat hunting capabilities regularly. This structured improvement plan allows organizations to move up the maturity levels and achieve their cybersecurity goals.
Technology and Automation
Organizations at the innovative stage develop custom data analysis techniques and have skilled threat hunters to isolate advanced threats. Leveraging technology and automation is key to moving up the Threat Hunting Maturity Model to detect and respond to sophisticated threats.
The leading stage has high automation of successful hunting processes, so analysts can focus on strategic improvements and overall security posture. Using advanced data analysis techniques and automated detection systems reduces false positives and improves threat detection accuracy.
Conclusion
The Threat Hunting Maturity Model is more than a framework; it's a roadmap to stronger, proactive security. By assessing your current level and advancing through the stages, you can reduce risks, improve detection, and respond faster. With the right tools, threat hunting becomes easier and more effective.
Ready to see it in action? Book a demo now and discover how our platform can help you advance through the HMM levels and build a stronger, more proactive security posture.
Hunt adversary infrastructure in real time. Surface C2 servers, enrich IOCs,
and map attacker activity at scale with our unified threat hunting platform.

Hunt adversary infrastructure in real time. Surface C2 servers, enrich IOCs,
and map attacker activity at scale with our unified threat hunting platform.

Hunt adversary infrastructure in real time. Surface C2 servers, enrich IOCs,
and map attacker activity at scale with our unified threat hunting platform.





