Threat Hunting Loop: From First Hypothesis to Final Action
Published on Oct 23, 2025

At Hunt.io, threat hunting is not an occasional project; it is part of our daily routine, and we live and breathe threat hunting. We track live C2 infrastructure, map attacker tactics, and chase data anomalies that automated systems often overlook. This hands-on exposure to intrusions has shaped how we approach the threat hunting loop.
The practice is also growing industry-wide: according to Intel471 (citing the SANS 2025 Threat Hunting Survey), the number of organizations managing threat hunting internally rose to 58%, up from 45% in 2024. And with cybercrime costs projected to exceed $20 trillion globally by 2026, as indicated by Evolvesecurity, building a structured loop is more critical than ever.
In this landscape, our team at Hunt.io has built a structured loop that guides every hunt. Our loop follows five stages: hypothesis, data collection and analysis, deep dive, documentation and reporting, and iterative feedback. Each reinforces the other to give security teams a consistent way to detect and stop malicious activity before it escalates.
What is the Threat Hunting Loop?
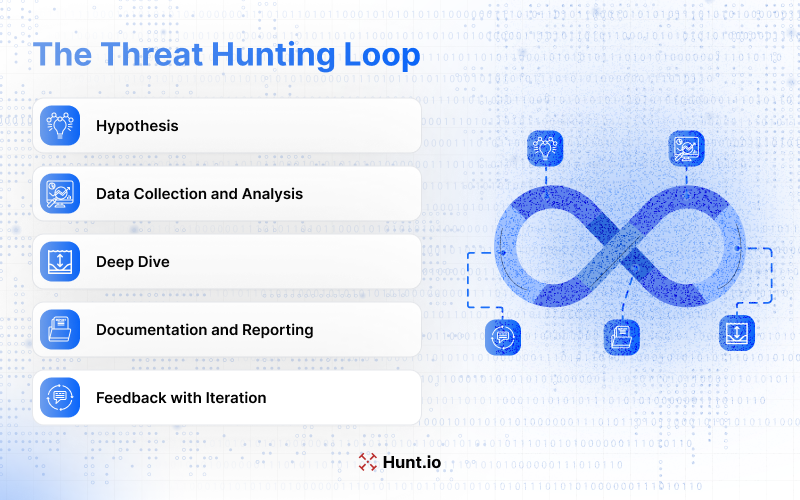
Threat hunting is a proactive, repeatable process designed to uncover threats that automated tools might miss. It relies on the hunter's ability to spot subtle signals in large datasets and connect them to the right context.
What makes it a loop is its cyclical nature. Hunters move through five stages, which are Hypothesis, Data Collection and Analysis, Deep Dive, Documentation and Reporting, and Feedback with Iteration, and then circle back, refining their approach with each pass.
Over time, this cycle not only helps uncover hidden threats but also builds collective knowledge, sharpening an organization's overall detection and response capabilities.
The Hypothesis Stage
A hunt begins with a hypothesis, an informed assumption about possible malicious activity. This can be based on recent threat intelligence, anomalies in network behavior, patterns in logs, or newly released indicators of compromise.
At Hunt.io, many hunts start from pivots on known malicious infrastructure, such as active command and control (C2) servers from our C2 feeds. From there, we branch out to connected domains, IP ranges, or ASN clusters, often writing custom HuntSQLTM queries to surface related assets.
Even when the original theory turns out to be incorrect, the process often reveals new infrastructure, samples of malware families, or techniques that were not previously detected.
Data Collection and Analysis
The success of a hunt depends heavily on the quality, relevance, and completeness of the data available. This can include network flow logs, endpoint telemetry, DNS history, file metadata, and curated threat intelligence reports. The goal is to gather data that is directly actionable rather than overwhelming analysts with noise.
We focus on integrating multiple datasets so analysts can start from a single IOC and quickly pivot into a complete infrastructure view. This makes correlation easier, speeds up validation, and helps separate background noise from meaningful signals.
Deep Dive
The deep dive is where the initial hypothesis is tested in detail. It requires a clear understanding of what normal activity looks like in the environment, which is essential to separating harmless anomalies from genuine threats.
Here at Hunt.io, this stage often involves building relationship graphs between indicators of compromise (IOCs), identifying command-and-control patterns, and looking for rare or suspicious connections over time. For example, discovering that a legitimate-looking subdomain is consistently resolving to known attacker IP ranges can be the link that turns a vague suspicion into confirmed malicious activity. Once validated, the focus turns to containment, eradication, and full infrastructure mapping to prevent re-entry.
Documentation
Accurate documentation is not simply an administrative step; it is a critical part of operational security. It records what was investigated, how evidence was gathered, and the results of the hunt. This ensures findings can be reviewed, acted upon, and referenced in the future.
At Hunt.io, we standardize documentation so it can be directly used to create new detection rules, feed IOC enrichment pipelines, or be shared in intelligence reports. This allows other defenders to act on the findings without having to reconstruct the investigation from scratch.
Feedback and Iteration
Closing the loop means reviewing the hunt to see what worked and what needs to be improved. This includes assessing data sources, evaluating the accuracy of the hypothesis, and identifying gaps in detection coverage.
We use feedback to adjust both methodology and tooling. If a hunt revealed that certain logs were unavailable or incomplete, that gap is addressed before the next cycle begins. Over time, this creates a threat hunting process that is both more efficient and better suited to the evolving tactics of attackers.
Understanding the loop in theory is one thing, but seeing it applied makes the concept real. By walking through concrete investigations, we can show you how each stage comes together in practice.
The Threat Hunting Loop in Action: Real Examples
We apply the threat hunting loop daily in investigations that range from targeted infrastructure mapping to uncovering malware delivery chains. The following are examples from our own research that show how the loop moves from initial hypothesis to final action.
Cobalt Strike PowerShell Loader Investigation

A suspicious PowerShell loader discovered in an open directory set the hypothesis in motion. Analysis revealed reflective in-memory execution and connections to active Cobalt Strike command-and-control servers. We validated these findings using SSL certificate metadata, documented all related IOCs, and used them to refine detection rules for future hunts.
Watermark-Based Cobalt Strike Mapping
A rare watermark embedded in a Cobalt Strike payload became the starting point for a hunt. We traced servers sharing that watermark, reviewed associated beacon configurations, and collected payload hashes. Documentation is fed directly into our detection pipelines, improving monitoring for similar infrastructure.

We began with a hypothesis based on deceptive clipboard and prompt behaviors linked to ClickFix exploitation. Using targeted HuntSQLTM queries, we identified active domains delivering malicious payloads. Findings were recorded with IOCs and served as input for updating detection logic.
These cases demonstrate how the loop's stages connect in practice, and how each investigation feeds improvements back into the process, but not every hunt succeeds just because the steps are followed. The real difference comes from what powers the loop: the skills of the hunters, the tools at their disposal, and the processes that tie it all together.
What Makes Successful Threat Hunting
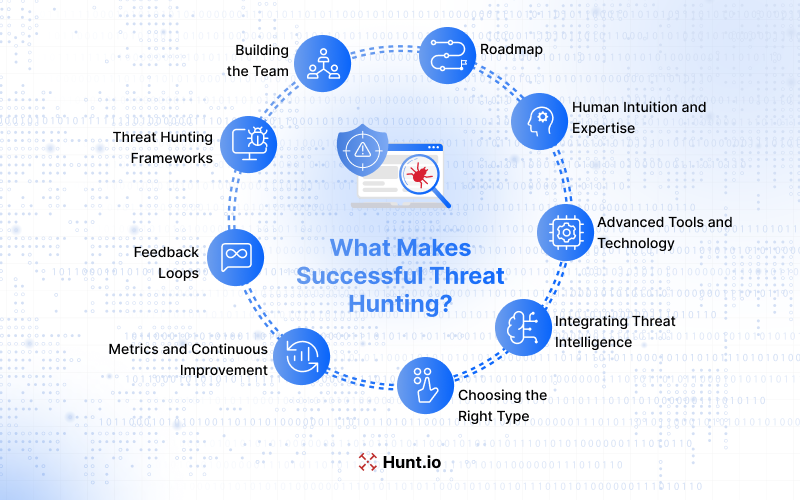
Successful threat hunting relies on more than just tools; it's a combination of skill, experience, and process. Understanding what drives effective hunts helps teams focus their efforts, optimize outcomes, and continuously refine their approach.
Human Intuition and Expertise
Human intuition, backed by experience, is essential for connecting fragmented or incomplete data points. Our team has developed these skills over years of tracking threat actor campaigns and infrastructure. Each member brings expertise in areas such as network forensics, malware reverse engineering, and large-scale data analysis, allowing us to tackle hunts from multiple angles.
Advanced Tools and Technology
Effective hunting uses the right combination of threat hunting platforms and in-house threat hunting tools. We use SIEM systems, EDR solutions, and our HuntSQLTM interface to query, pivot, and visualize results. Machine learning models assist in identifying anomalies, but analyst review ensures context is applied before action is taken. Centralized data storage with standardized formats is key to enabling fast, repeatable, and collaborative analysis.
Enter Hunt.io Threat Hunting Platform
Our high-performance threat hunting platform brings all the features that your team needs and much more, all together in a single environment. With Hunt.io, analysts can move seamlessly from hypothesis to action, reducing dwell time and strengthening defenses with every cycle.
We've designed Hunt.io to give your team more than just data: we provide context, clarity, and the ability to act fast. Our continuously updated C2 infrastructure feed and IOC Hunter deliver indicators you can trust, backed by first-party validation.
With AttackCapture™, we help you uncover hidden threats in exposed directories, while our phishing infrastructure monitoring keeps you ahead of malicious campaigns before they strike. To make investigations even faster, we developed HuntSQLTM, our powerful query engine that lets analysts search, filter, and pivot across massive datasets in seconds.
Every feature is built to work together, empowering analysts to spend less time stitching information across tools and more time stopping real threats. And with our Threat Enrichment API, you can integrate Hunt.io intelligence directly into your workflows, giving your security operations the edge they need to stay proactive.
Integrating Threat Intelligence
Threat intelligence feeds supply the raw intelligence that, when analyzed, provides the context hunters need to prioritize leads. We combine intelligence from our own research with multiple external feeds, giving a more complete picture of both current threats and emerging infrastructure.
Frameworks like TaHiTI recommend using knowledge of known threats to guide hunting, and in practice, this shortens the time from lead to detection.
Choosing the Right Type
Structured hunting is one of the main types of threat hunting and follows predefined playbooks, making it ideal for repeatable processes. It is measurable and easier to scale across teams, but the trade-off is that unexpected activity may be missed if it falls outside the set scope.
Unstructured hunting starts with an anomaly, a hunch, or a pattern noticed in the data. It is flexible and can uncover unique attack methods, but it requires more time and effort to validate leads, and its results can be harder to measure.
Metrics and Continuous Improvement
Tracking key metrics such as the number of detections created, dwell time reduction, and false positive rates helps measure the impact of the hunting program. Frameworks like PEAK emphasize that metrics should guide decision-making and help set improvement priorities.
Improve Detection Rules
Every hunt should produce findings that can be fed back into automated detection. This includes adding new rules, refining existing ones, and reducing false positives. Keeping detection logic current ensures alerts remain accurate and relevant.
Measure Success
Beyond hard metrics, always gather feedback from the hunting team after each cycle. Analysts can identify workflow bottlenecks, tooling issues, or data blind spots that may not be visible in the metrics alone. This ensures both qualitative and quantitative improvements.
Feedback Loops
Regular debriefs after hunts are essential for knowledge sharing and for refining processes. By sharing what worked, what failed, and what needs to change, the entire team benefits from each hunt's lessons.
Threat Hunting Frameworks
Threat hunting frameworks such as MITRE ATT&CK, PEAK, Sqrrl, and TaHiTI offer tested methodologies for organizing hunts. We adapt these to our environment and the specific threats we track, ensuring the process is both relevant and practical.
Choose the Right Framework
The right framework depends on the organization's size, maturity, and threat profile. Many teams combine elements from several frameworks to create an approach that fits their operational needs.
Build a Hunting Team
An effective hunting team is built around complementary skills. This means including analysts, incident responders, and data specialists who can work together to take an investigation from a single clue to complete resolution.
Create a Roadmap
A roadmap defines how hunting capabilities will grow, including the addition of new data sources, improved tooling, and expanded analysis techniques. This helps ensure that growth is deliberate and aligned with long-term security goals.
Of course, even the best-equipped teams face obstacles. Addressing them head-on is what separates efficient hunting programs from those that struggle to deliver results.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Threat Hunting

Threat hunting delivers strong results, but it's not without hurdles. Teams often face recurring challenges that, if not addressed, can slow down hunts or limit their impact.
False Positives
High false positive rates can drain resources. Reducing them requires better context in alerts, improved detection logic, and cross-team validation before escalation.
Handling Big Data
Security data is often vast and complex. Centralizing it, indexing it efficiently, and allowing flexible pivots between datasets ensures analysts can find meaningful patterns without losing time on irrelevant noise.
Skill Gaps
Effective hunting demands expertise in multiple domains: network forensics, malware analysis, and data science, to name a few. Addressing skill gaps through training, mentorship, and cross-functional collaboration ensures hunts remain thorough and actionable.
Wrapping up
Mastering the threat hunting loop requires more than following a checklist. It calls for a clear process, a skilled team, and the ability to adapt techniques as threats evolve.
At Hunt.io, we have learned that combining structured methodologies with the freedom to pursue anomalies produces the most reliable results. This approach allows us to uncover threats that automated systems miss, refine detection logic with every cycle, and strengthen defenses continuously.
Now is the time to take your threat hunting loop to the next level. Book a demo now and see how we can help refine and strengthen every stage of your process.
At Hunt.io, threat hunting is not an occasional project; it is part of our daily routine, and we live and breathe threat hunting. We track live C2 infrastructure, map attacker tactics, and chase data anomalies that automated systems often overlook. This hands-on exposure to intrusions has shaped how we approach the threat hunting loop.
The practice is also growing industry-wide: according to Intel471 (citing the SANS 2025 Threat Hunting Survey), the number of organizations managing threat hunting internally rose to 58%, up from 45% in 2024. And with cybercrime costs projected to exceed $20 trillion globally by 2026, as indicated by Evolvesecurity, building a structured loop is more critical than ever.
In this landscape, our team at Hunt.io has built a structured loop that guides every hunt. Our loop follows five stages: hypothesis, data collection and analysis, deep dive, documentation and reporting, and iterative feedback. Each reinforces the other to give security teams a consistent way to detect and stop malicious activity before it escalates.
What is the Threat Hunting Loop?

Threat hunting is a proactive, repeatable process designed to uncover threats that automated tools might miss. It relies on the hunter's ability to spot subtle signals in large datasets and connect them to the right context.
What makes it a loop is its cyclical nature. Hunters move through five stages, which are Hypothesis, Data Collection and Analysis, Deep Dive, Documentation and Reporting, and Feedback with Iteration, and then circle back, refining their approach with each pass.
Over time, this cycle not only helps uncover hidden threats but also builds collective knowledge, sharpening an organization's overall detection and response capabilities.
The Hypothesis Stage
A hunt begins with a hypothesis, an informed assumption about possible malicious activity. This can be based on recent threat intelligence, anomalies in network behavior, patterns in logs, or newly released indicators of compromise.
At Hunt.io, many hunts start from pivots on known malicious infrastructure, such as active command and control (C2) servers from our C2 feeds. From there, we branch out to connected domains, IP ranges, or ASN clusters, often writing custom HuntSQLTM queries to surface related assets.
Even when the original theory turns out to be incorrect, the process often reveals new infrastructure, samples of malware families, or techniques that were not previously detected.
Data Collection and Analysis
The success of a hunt depends heavily on the quality, relevance, and completeness of the data available. This can include network flow logs, endpoint telemetry, DNS history, file metadata, and curated threat intelligence reports. The goal is to gather data that is directly actionable rather than overwhelming analysts with noise.
We focus on integrating multiple datasets so analysts can start from a single IOC and quickly pivot into a complete infrastructure view. This makes correlation easier, speeds up validation, and helps separate background noise from meaningful signals.
Deep Dive
The deep dive is where the initial hypothesis is tested in detail. It requires a clear understanding of what normal activity looks like in the environment, which is essential to separating harmless anomalies from genuine threats.
Here at Hunt.io, this stage often involves building relationship graphs between indicators of compromise (IOCs), identifying command-and-control patterns, and looking for rare or suspicious connections over time. For example, discovering that a legitimate-looking subdomain is consistently resolving to known attacker IP ranges can be the link that turns a vague suspicion into confirmed malicious activity. Once validated, the focus turns to containment, eradication, and full infrastructure mapping to prevent re-entry.
Documentation
Accurate documentation is not simply an administrative step; it is a critical part of operational security. It records what was investigated, how evidence was gathered, and the results of the hunt. This ensures findings can be reviewed, acted upon, and referenced in the future.
At Hunt.io, we standardize documentation so it can be directly used to create new detection rules, feed IOC enrichment pipelines, or be shared in intelligence reports. This allows other defenders to act on the findings without having to reconstruct the investigation from scratch.
Feedback and Iteration
Closing the loop means reviewing the hunt to see what worked and what needs to be improved. This includes assessing data sources, evaluating the accuracy of the hypothesis, and identifying gaps in detection coverage.
We use feedback to adjust both methodology and tooling. If a hunt revealed that certain logs were unavailable or incomplete, that gap is addressed before the next cycle begins. Over time, this creates a threat hunting process that is both more efficient and better suited to the evolving tactics of attackers.
Understanding the loop in theory is one thing, but seeing it applied makes the concept real. By walking through concrete investigations, we can show you how each stage comes together in practice.
The Threat Hunting Loop in Action: Real Examples
We apply the threat hunting loop daily in investigations that range from targeted infrastructure mapping to uncovering malware delivery chains. The following are examples from our own research that show how the loop moves from initial hypothesis to final action.
Cobalt Strike PowerShell Loader Investigation

A suspicious PowerShell loader discovered in an open directory set the hypothesis in motion. Analysis revealed reflective in-memory execution and connections to active Cobalt Strike command-and-control servers. We validated these findings using SSL certificate metadata, documented all related IOCs, and used them to refine detection rules for future hunts.
Watermark-Based Cobalt Strike Mapping

A rare watermark embedded in a Cobalt Strike payload became the starting point for a hunt. We traced servers sharing that watermark, reviewed associated beacon configurations, and collected payload hashes. Documentation is fed directly into our detection pipelines, improving monitoring for similar infrastructure.

We began with a hypothesis based on deceptive clipboard and prompt behaviors linked to ClickFix exploitation. Using targeted HuntSQLTM queries, we identified active domains delivering malicious payloads. Findings were recorded with IOCs and served as input for updating detection logic.
These cases demonstrate how the loop's stages connect in practice, and how each investigation feeds improvements back into the process, but not every hunt succeeds just because the steps are followed. The real difference comes from what powers the loop: the skills of the hunters, the tools at their disposal, and the processes that tie it all together.
What Makes Successful Threat Hunting

Successful threat hunting relies on more than just tools; it's a combination of skill, experience, and process. Understanding what drives effective hunts helps teams focus their efforts, optimize outcomes, and continuously refine their approach.
Human Intuition and Expertise
Human intuition, backed by experience, is essential for connecting fragmented or incomplete data points. Our team has developed these skills over years of tracking threat actor campaigns and infrastructure. Each member brings expertise in areas such as network forensics, malware reverse engineering, and large-scale data analysis, allowing us to tackle hunts from multiple angles.
Advanced Tools and Technology
Effective hunting uses the right combination of threat hunting platforms and in-house threat hunting tools. We use SIEM systems, EDR solutions, and our HuntSQLTM interface to query, pivot, and visualize results. Machine learning models assist in identifying anomalies, but analyst review ensures context is applied before action is taken. Centralized data storage with standardized formats is key to enabling fast, repeatable, and collaborative analysis.
Enter Hunt.io Threat Hunting Platform
Our high-performance threat hunting platform brings all the features that your team needs and much more, all together in a single environment. With Hunt.io, analysts can move seamlessly from hypothesis to action, reducing dwell time and strengthening defenses with every cycle.

We've designed Hunt.io to give your team more than just data: we provide context, clarity, and the ability to act fast. Our continuously updated C2 infrastructure feed and IOC Hunter deliver indicators you can trust, backed by first-party validation.
With AttackCapture™, we help you uncover hidden threats in exposed directories, while our phishing infrastructure monitoring keeps you ahead of malicious campaigns before they strike. To make investigations even faster, we developed HuntSQLTM, our powerful query engine that lets analysts search, filter, and pivot across massive datasets in seconds.
Every feature is built to work together, empowering analysts to spend less time stitching information across tools and more time stopping real threats. And with our Threat Enrichment API, you can integrate Hunt.io intelligence directly into your workflows, giving your security operations the edge they need to stay proactive.
Integrating Threat Intelligence
Threat intelligence feeds supply the raw intelligence that, when analyzed, provides the context hunters need to prioritize leads. We combine intelligence from our own research with multiple external feeds, giving a more complete picture of both current threats and emerging infrastructure.
Frameworks like TaHiTI recommend using knowledge of known threats to guide hunting, and in practice, this shortens the time from lead to detection.
Choosing the Right Type
Structured hunting is one of the main types of threat hunting and follows predefined playbooks, making it ideal for repeatable processes. It is measurable and easier to scale across teams, but the trade-off is that unexpected activity may be missed if it falls outside the set scope.
Unstructured hunting starts with an anomaly, a hunch, or a pattern noticed in the data. It is flexible and can uncover unique attack methods, but it requires more time and effort to validate leads, and its results can be harder to measure.
Metrics and Continuous Improvement
Tracking key metrics such as the number of detections created, dwell time reduction, and false positive rates helps measure the impact of the hunting program. Frameworks like PEAK emphasize that metrics should guide decision-making and help set improvement priorities.
Improve Detection Rules
Every hunt should produce findings that can be fed back into automated detection. This includes adding new rules, refining existing ones, and reducing false positives. Keeping detection logic current ensures alerts remain accurate and relevant.
Measure Success
Beyond hard metrics, always gather feedback from the hunting team after each cycle. Analysts can identify workflow bottlenecks, tooling issues, or data blind spots that may not be visible in the metrics alone. This ensures both qualitative and quantitative improvements.
Feedback Loops
Regular debriefs after hunts are essential for knowledge sharing and for refining processes. By sharing what worked, what failed, and what needs to change, the entire team benefits from each hunt's lessons.
Threat Hunting Frameworks
Threat hunting frameworks such as MITRE ATT&CK, PEAK, Sqrrl, and TaHiTI offer tested methodologies for organizing hunts. We adapt these to our environment and the specific threats we track, ensuring the process is both relevant and practical.
Choose the Right Framework
The right framework depends on the organization's size, maturity, and threat profile. Many teams combine elements from several frameworks to create an approach that fits their operational needs.
Build a Hunting Team
An effective hunting team is built around complementary skills. This means including analysts, incident responders, and data specialists who can work together to take an investigation from a single clue to complete resolution.
Create a Roadmap
A roadmap defines how hunting capabilities will grow, including the addition of new data sources, improved tooling, and expanded analysis techniques. This helps ensure that growth is deliberate and aligned with long-term security goals.
Of course, even the best-equipped teams face obstacles. Addressing them head-on is what separates efficient hunting programs from those that struggle to deliver results.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Threat Hunting

Threat hunting delivers strong results, but it's not without hurdles. Teams often face recurring challenges that, if not addressed, can slow down hunts or limit their impact.
False Positives
High false positive rates can drain resources. Reducing them requires better context in alerts, improved detection logic, and cross-team validation before escalation.
Handling Big Data
Security data is often vast and complex. Centralizing it, indexing it efficiently, and allowing flexible pivots between datasets ensures analysts can find meaningful patterns without losing time on irrelevant noise.
Skill Gaps
Effective hunting demands expertise in multiple domains: network forensics, malware analysis, and data science, to name a few. Addressing skill gaps through training, mentorship, and cross-functional collaboration ensures hunts remain thorough and actionable.
Wrapping up
Mastering the threat hunting loop requires more than following a checklist. It calls for a clear process, a skilled team, and the ability to adapt techniques as threats evolve.
At Hunt.io, we have learned that combining structured methodologies with the freedom to pursue anomalies produces the most reliable results. This approach allows us to uncover threats that automated systems miss, refine detection logic with every cycle, and strengthen defenses continuously.
Now is the time to take your threat hunting loop to the next level. Book a demo now and see how we can help refine and strengthen every stage of your process.
Hunt adversary infrastructure in real time. Surface C2 servers, enrich IOCs,
and map attacker activity at scale with our unified threat hunting platform.

Hunt adversary infrastructure in real time. Surface C2 servers, enrich IOCs,
and map attacker activity at scale with our unified threat hunting platform.

Hunt adversary infrastructure in real time. Surface C2 servers, enrich IOCs,
and map attacker activity at scale with our unified threat hunting platform.





